Injection molding polystyrene is a widely utilized process in the plastics manufacturing industry, known for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency in producing custom made plastic parts. This comprehensive guide explores polystyrene material properties and the PS injection molding process-related knowledge.
Overview of Polystyrene Plastic

Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic thermoplastic derived from styrene monomers. It exhibits excellent clarity, rigidity, and lightweight characteristics in its pure form. Its amorphous structure ensures excellent flow, enabling precise replication of intricate designs.
Classification of Polystyrene
- General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), known for its high transparency, is rigid but relatively brittle.
- High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS), enhanced with rubber additives, provides toughness and impact resistance.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a foam-type PS often used for lightweight packaging and insulation.
- Syndiotactic Polystyrene (SPS), a crystalline form, excels in heat and chemical resistance for engineering applications.
Key Performance Properties of PS
- Clarity: GPPS boasts 90% light transmissibility, making it a cost-effective alternative to glass for transparent products.
- Lightweight: With a density of 1.04-1.09 g/cm³, PS reduces product weight, lowering shipping and material costs.
- Moisture Resistance: PS does not absorb water, maintaining dimensional stability even in humid environments.
- Chemical Resistance: PS resists acids and bases but is vulnerable to solvents, requiring careful environmental consideration.
- Radiation Resistance: Capable of withstanding gamma radiation up to 10,000 kGy, PS is ideal for sterilized medical components.
PS Injection Molding Process
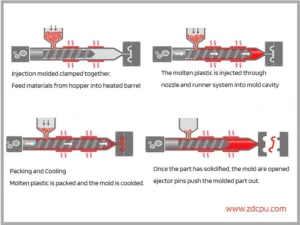
The PS injection molding process transforms raw polystyrene pellets into precise components through a series of meticulously controlled steps:
- Material Preparation: PS pellets are loaded into the machine’s hopper. Pre-drying is typically unnecessary unless using recycled material or operating in high-humidity conditions.
- Melting: Pellets are melted in the injection molding machine’s barrel at temperatures usually ranging from 180°C to 270°C.
- Injection and Packing: Molten PS is injected into the mold cavity under proper pressures, filling intricate geometries with precision.
- Cooling: The mold remains at a temperature between 40°C to 80°C, allowing the part to solidify.
- Ejection: Solidified parts are ejected using pins or air blasts, facilitated by draft angles and surface finishes for easy removal.
- Post-Processing: Parts may undergo trimming, painting, or assembly to meet final specifications.
Advantages of PS Injection Molding
Using PS for injection molding offers multiple benefits:
- Excellent Flow Characteristics: PS’s low melt viscosity facilitates molding of intricate shapes and fine features.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to other engineering plastics, PS is budget-friendly while delivering adequate mechanical properties.
- High Dimensional Stability: Low shrinkage rates (typically 0.2% to 0.8%) ensure precision in molded parts.
- Broad Processing Temperature Range: PS adapts well to processing temperatures approximately between 180°C and 270°C.
- Versatility: Applicable for creating both rigid and foam products with variations in toughness and transparency.

PS Injection Molding Service
PS vs Other Plastics: Key Differences in Injection Molding
When selecting materials for injection molding polystyrene, understanding how PS compares to other plastics is essential:
- Polystyrene vs. Polypropylene (PP) Injection Molding: PS offers superior clarity and rigidity but lower impact resistance and heat tolerance. PP suits flexible, durable parts, while PS excels in transparent, cost-effective applications.
- Polystyrene vs. Polyethylene (PE) Injection Molding: PS has better dimensional stability and a higher melting point but is less flexible. PE’s toughness suits rugged uses, while PS is preferred for rigid, clear parts.
- Polystyrene vs. Polycarbonate (PC) Injection Molding: PC is tougher and more heat-resistant but significantly costlier. PS molding is ideal for disposable, transparent items where cost is a priority.
- Polystyrene vs. ABS Injection Molding: ABS provides better impact resistance and heat stability, but PS is cheaper and clearer, making it suitable for aesthetic-focused applications.
Complete PS Injection Molding Operation Guide
Achieving optimal results in polystyrene PS injection molding requires adherence to best practices across machine selection, processing parameters, and mold design:
Machine Selection
Opt for an injection molding machine with a screw L/D ratio of 17-24 and a compression ratio of 1.6-4.0 to ensure smooth material flow and consistent melting.
Temperature Settings
- Barrel and Nozzle: Typically set between 180°C and 270°C. Avoid exceeding 280°C to prevent degradation.
- Mold Temperature: Maintained between 40°C to 80°C to promote adequate cooling without warping.
Injection Pressure
Recommended between 60 MPa to 150 MPa, depending on part complexity and size.
PS Injection Molding Parts Design
- Wall Thickness: Design parts with 1-3 mm thickness, with transitions under 25% to prevent defects like sink marks or voids.
- Draft Angles: Use 0.5-1° for GPPS and 1-2° for HIPS to facilitate easy ejection and reduce stress.
- Gate Design: Employ edge gates (0.5-1.5 mm) for GPPS to minimize flow marks and sub-gates for HIPS to enhance aesthetics.
- Venting: Incorporate vents (0.02-0.05 mm) to prevent burn marks and ensure complete mold filling.
- Ribs and Stiffeners: Designed at 50-60% of wall thickness to avoid sink marks.
- Fillets and Radii: Minimum radius about 25% of wall thickness to reduce stress concentration, especially for GPPS.
Material Selection
Choose GPPS for applications requiring clarity, HIPS for durability, or EPS for lightweight insulation, aligning with mechanical and environmental needs.
Applications of PS Injection Molding

Polystyrene PS injection molding supports manufacturing in diverse sectors:
- Medical: Laboratory consumables like petri dishes, test tubes, lab vials, and diagnostic equipment.
- Packaging: Food containers, disposable cutlery, and protective packaging foam.
- Automotive: interior trims, dashboards, and panels.
- Consumer Electronics: Housings for remote controls, insulators, and other components.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, appliance housings, and CD cases.
Zhongde Custom PS Injection Molding Services
For seeking quality PS molding solutions, Zhongde offers expert custom PS injection molding services. The dedicated team provides support for material selection, mold design consultation, and efficient production.
FAQ
Polystyrene is a good choice when you need a lightweight, cost-effective plastic with good dimensional stability and clarity, such as packaging, consumer goods, or medical components.
Common defects of plastic parts include warpage, sink marks, brittleness leading to cracking, and surface blemishes. These can be prevented by controlling wall thickness (keeping it uniform and moderate), using adequate mold temperatures and cooling times, applying appropriate draft angles for easy ejection, and selecting the right grade of PS. Additionally, maintaining proper injection pressure and drying the material if needed helps avoid defects.
PS is recyclable, and many injection molded PS products can be reused or recycled. However, it is not biodegradable, so environmental impact depends on waste management practices.