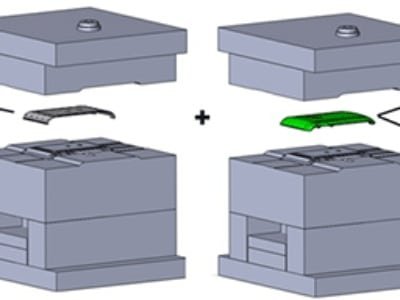
Within Injection mold, mold inserts are critical components that enhance mold functionality, simplify manufacturing, and improve product quality. This article delves into the definition, types, materials, functions, design considerations, and manufacturing of mold inserts, providing a detailed understanding of their role in injection molds.
What Are Mold Inserts?
Mold inserts are precision-made components embedded within the mold cavity or core to form specific features of the molded part or to facilitate mold manufacturing and maintenance. Mold inserts are part of the mold itself. They can be removable or permanent, designed to be replaced or serviced independently of the main mold structure. They are widely used in complex applications such as insert molding service, where one material is molded around another pre-placed component. Learn more about what is insert molding to understand how mold inserts contribute to multi-material designs.
Mold inserts serve to simplify the machining of complex geometries, improve mold venting, enable easy repair of wear-prone areas, and optimize thermal management within the mold. Their use is essential in achieving high-quality molded parts while reducing mold fabrication time and cost.
Common Materials for Mold Inserts
The Mold insert lies in its material, chosen for durability under intense molding conditions. Common options include:
Tool Steel (P20, H13): Renowned for wear resistance, ideal for high-volume molds.
Aluminum: Used in low-volume or prototype molds due to ease of machining but less durable.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, perfect for medical or food-grade applications.
Beryllium Copper: Exceptional thermal conductivity, used in mold in inserts for cooling-critical molds.
Types of Mold Inserts
Mold inserts come in diverse forms, each tailored to specific molding needs:
- Cores: Shape internal features, like the hollow of an automotive gear.
- Cavity Inserts: Form external part surfaces, ensuring smooth finishes.
- Sliders: Enable side-action features, such as undercuts in connectors.
- Blocks: Support localized molding, ideal for intricate details.
- Cooling Inserts: Enhance thermal management, often using beryllium copper.
- Vent Inserts: Specially designed inserts that facilitate venting by allowing trapped air to escape from the mold cavity.
- Pin Inserts: Small, cylindrical inserts used to create holes or thin features in the molded part.
- Standard Inserts: Pre-manufactured components with common shapes like holes, slots, or textured surfaces.
- Custom Inserts: Includes angled, tapered, or irregularly shaped inserts designed for unique mold features or to ease assembly and disassembly.
Limitations and Challenges of Mold Inserts
While mold inserts offer many benefits, they also present challenges:
- Structural Integrity: Improperly designed inserts can weaken the mold structure, leading to deformation or failure under injection pressures.
- Assembly Complexity: Precise alignment and tight tolerances are required to ensure inserts fit securely and maintain dimensional accuracy.
- Cooling Channel Design: Insert placement can complicate cooling channel routing, potentially increasing cycle times if not carefully planned.
- Surface Marks: Insert parting lines or seams may leave visible marks on molded parts, which may require additional finishing or client approval.
Processing Mold Inserts
Mold inserts are typically manufactured using high-precision machining processes, we usually use different manufacturing processes based on different mold inserts:
CNC Machining: Shapes CNC molded inserts to tolerances as tight as ±0.01mm.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Carves intricate details, like fine cavities.
Wire Cutting: Ensures sharp edges for sliders or blocks.
Surface Treatment: Polishing or coatings enhance durability and release properties.
In Zhongde every molded in insert undergoes rigorous quality checks to meet stringent standards. Our expertise shines in non-standard mold inserts, crafting bespoke solutions for unique geometries or materials.
Key Design Considerations for Mold Inserts in Injection Molds
Effective mold insert design requires attention to multiple factors:
Venting: Inserts should be positioned to optimize air release and prevent defects like short shots or burn marks.
Material Compatibility: Insert materials should match or complement the mold base to avoid corrosion or thermal mismatch.
Thermal Conductivity: Strategic use of copper alloy inserts in high-heat areas can improve cooling uniformity.
Ease of Replacement: Inserts must be designed for quick removal and installation to minimize mold downtime.
Structural Strength: Avoid stress concentrations by designing smooth transitions and proper support around inserts.
Precision Mounting: Incorporate locating pins, grooves, or hang tabs to ensure repeatable and secure positioning.
Finding a Supplier Focused on Mold Details
Injection molding is a procesion process, and the injection mold is the core of injeciton molding process. So, choosing a supplier focused on mold details is pivotal. The parter with advanced CNC machined part capabilities to ensure the mold inserts meet tight tolerances. Zhongde with advanced CNC turning, milling, and EDM for tight tolerances. Contact us for your new projects.