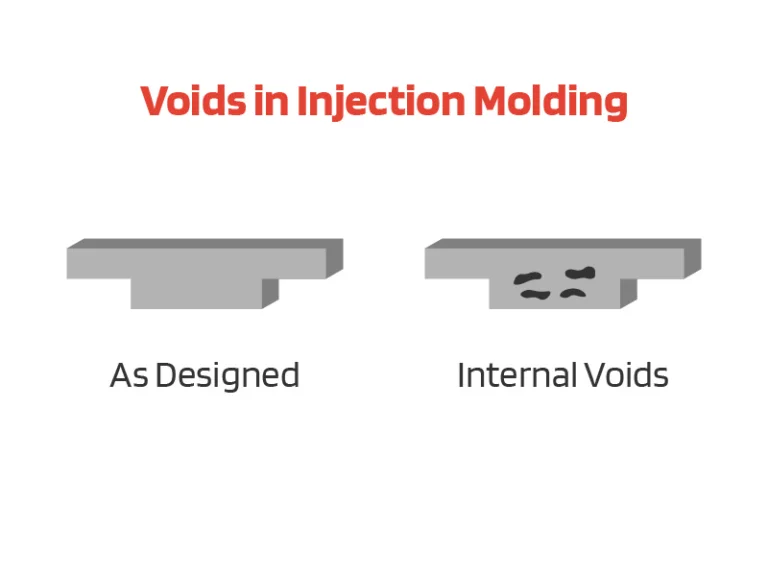
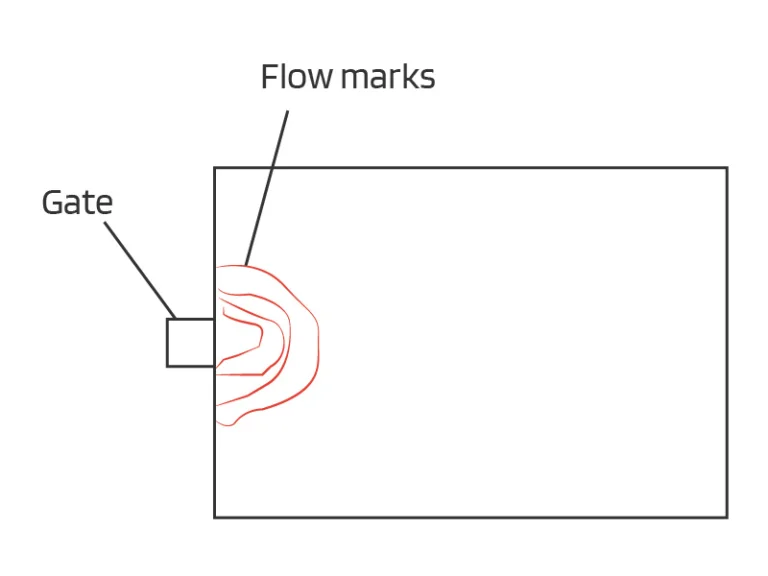
Plastic parts rib design is a critical element in ensuring the strength, functionality, and efficiency of the final product. In this post, we’ll explore the principle of rib design and its benefits, emphasizing practical insights for crafting robust plastic components.
What are Ribs in Plastic Molding?
Ribs, in the context of plastic molding, are structural features incorporated into the design of plastic parts. They are thin, elongated projections that extend perpendicularly from the walls or surfaces of a plastic component. These ribs are strategically placed to provide reinforcement, improve rigidity, and distribute loads effectively within the part. Rib design in plastic parts is crucial because it significantly enhances the strength and performance of plastic parts.
What are the Types of Ribs in Plastic Parts?
Long Grid Ribs:

Long grid ribs are a variation where ribs are arranged in a grid pattern, typically forming a lattice-like structure across the surface of the plastic part. This design provides comprehensive reinforcement, distributing loads evenly and adding stiffness to the entire area. Long grid ribs are often used in large, flat components, such as panels or enclosures, to prevent warping and maintain dimensional stability.
Circular Ribs:
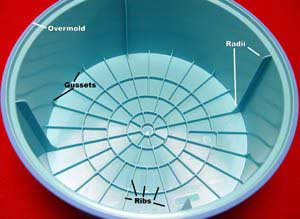
Circular ribs are ribs with a circular or radial pattern. They are commonly found in components with a circular or cylindrical shape, such as pipe fittings, tanks, or round covers. Circular ribs offer radial support and help distribute stress uniformly, making them suitable for applications with rotational forces.
Ribs Placed on the Corners:
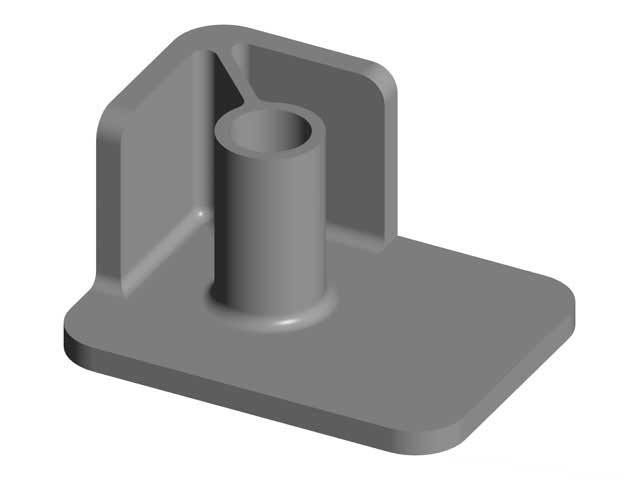
Ribs placed on the corners of a plastic part are strategically located to reinforce the edges and corners. These ribs enhance the part’s resistance to deformation and impact. This design is often used in cases where the corners are vulnerable to stress concentration or damage.
Ribs Placed on the Side Walls:

Ribs placed on the side walls of a plastic part serve to add rigidity and support to the vertical surfaces. These ribs can prevent buckling or flexing of the side walls, ensuring that the part retains its shape and structural integrity. They are commonly used in containers, housings, and similar components.
The Importance of Plastic Parts Ribs Design
Reduced Material Usage:
Well-designed ribs allow for the creation of strong plastic parts with less material. This not only reduces production costs but also minimizes environmental impact by conserving resources. It’s a sustainable approach to manufacturing.
Prevention of Warpage:
Ribs play a critical role in preventing warping and distortion in plastic parts. Ribs often extend from one surface of the plastic part to the other. Thick wall thickness cools more slowly, while thin wall thickness cools more rapidly. Ribs bridge this gap, ensuring uniform cooling across the entire part. This is especially important in applications like automotive components and electronics housings.
Support for Other Features:
Ribs can serve as a foundation for attaching additional features or components to a plastic part. For example, they can provide mounting points for fasteners, brackets, or electronic components, adding versatility to the design.
Improved Mold Flow:
Properly designed ribs enhance the flow of molten plastic during the injection molding process. This results in better filling of the mold cavity, reduced chances of defects like voids or sink marks, and improved overall part quality.
Factors to be Considered in Plastic Parts Rib Design
Rib Thickness:
The rib thickness should be smaller than the wall thickness of the plastic material. This is a crucial principle because it ensures that ribs don’t overpower the part, leading to issues like sink marks or excessive material usage. The recommended rib size being 0.4-0.5 times the thickness of the plastic material strikes a balance between reinforcement and material efficiency.
To get a comprehensive understanding of wall thickness design in injection molding, view our post: Injection Molding Wall Thickness Guideline: Maintain Uniform Wall Thickness of Injection Molded Plastic Parts
Click here to learn more about wall thickness.
Rib Height:
Rib height should be no more than 3 times the wall thickness. Limiting the rib height prevents excessive stress concentration and potential warpage in the plastic part. It also helps maintain uniform cooling during the molding process, reducing the risk of deformations.
Rib Spacing:
Rib spacing should be at least 2 times the wall thickness. Adequate rib spacing ensures that the material flows evenly during injection molding and that there are no voids or sink marks. It contributes to the structural integrity of the part and helps maintain dimensional stability.
Rib Draft:
A minimum 1-degree draft on ribs is essential. Draft angles facilitate the ejection of the part from the mold and prevent damage. For ribs, this draft angle ensures smooth and damage-free removal from the mold, reducing the likelihood of defects.
To get a deeper understanding of draft angle design for injection molding parts, read our post: Enhancing Part Quality by Optimizing Injection Molding Draft Angle Design
Rib Coring:
Rib coring involves removing material from the interior of the rib structure to reduce weight while maintaining strength. This is particularly relevant in applications where weight reduction is critical. Coring can help achieve the desired structural properties without excessive material usage.
Rib Radii:
Radii at feature intersections should be a minimum of 0.5 – 1.0 times the nominal wall thickness. This principle ensures that stress concentrations at sharp corners are minimized. Rounded intersections distribute stress more evenly, reducing the risk of part failure.
Conclusion
Through this exploration, we’ve delved into the core principles that guide effective rib design, emphasizing the vital role it plays in enhancing plastic parts’ strength and overall quality. If you have any plastic molding needs or questions about rib design in plastic parts, we invite you to reach out to Zhongde, your trusted partner in manufacturing excellence.