The core and cavity in injection molding are fundamental components, which influence the quality, accuracy, functionality, and durability of the molded parts. Their proper design, construction, and maintenance are vital for achieving consistent and high-quality injection molded products. Today, we will learn about the cavity and core in injection molding, including the types, importance, and differences.
What Is Core and Cavity in Injection Molding?
In injection molding, the core and cavity are used to create the desired shape of the molded part. When the mold closes, the core and cavity come together to create the mold cavity, which is then filled with molten plastic to form the final part shape. The core and cavity need to be precisely designed and machined to ensure accurate part replication and proper molding conditions.
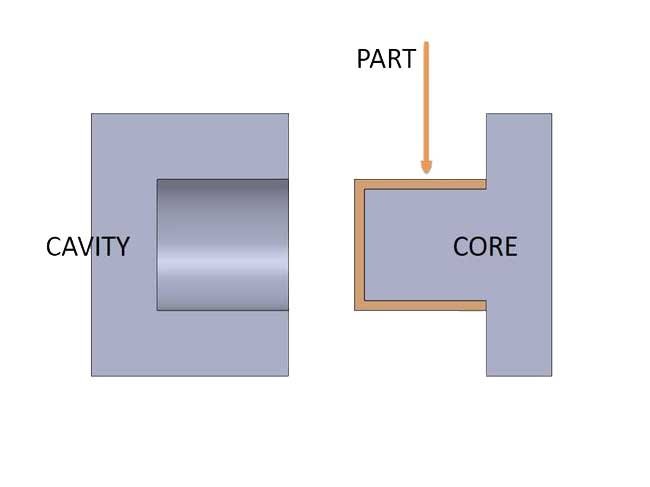
Cavity in Injection Molding
The cavity is the stationary part of the mold and forms the outer surface of the molded part. It determines the shape, texture, and appearance of the final product. The cavity is responsible for creating the desired aesthetics and dimensional accuracy of the part.
Core in Injection Molding
The core is the movable component that shapes the internal features of the part. It defines the intricate details, such as holes, recesses, and internal contours. The core moves within the mold to create the desired shape and geometry of the part’s interior.
The Importance of Core and Cavity in Injection Molding
Their importance of core and cavity in injection molding can be summarized as follows:
- Shape and Accuracy: The core and cavity define the shape and dimensions of the molded part. They are responsible for creating the desired features, details, and surface finish of the final product. Precise and well-designed core and cavity ensure accurate replication of the desired part geometry.
- Mold Functionality: The core and cavity play a critical role in the overall functionality of the mold. They enable the proper flow and distribution of the molten plastic material, ensuring consistent filling of the mold cavity. Properly designed and machined core and cavity allow for efficient and effective mold operation.
- Tooling Durability: The core and cavity experience high levels of stress and thermal cycles during the injection molding process. Therefore, they need to be made from durable and wear-resistant materials to withstand the demands of repeated molding cycles. Proper maintenance and quality construction of the core and cavity contribute to the longevity of the mold. View this post to understand other ways to expand mold lifespan.
- Cooling and Ejection: The core and cavity also contribute to the cooling and ejection processes. They incorporate cooling channels to dissipate heat from the molten plastic, aiding in solidification and cycle time optimization. Additionally, the cavity contains the ejection system, which helps remove the molded part from the mold after the cooling process.
Principle of Injection Molding Process
Types of Mold Cavities and Cores
In injection molds, there are many types of cavities, and cores can be categorized. There are some main types as bellow
1. Fixed Cavities and Cores:
Standard Cavities and Cores: These are the primary components of the mold that define the shape and features of the molded part. They are typically machined from hardened steel and remain fixed in the mold throughout the production process.
Simple Cavity/Core: This type of cavity and core is used for producing parts with straightforward shapes and minimal internal features. It consists of a single cavity and core component.
Multi-Cavity/Core: In this configuration, multiple cavities and cores are arranged within the mold to enable the simultaneous production of multiple parts in each molding cycle. It increases production efficiency and reduces cycle time.
2. Interchangeable Cavity/Core:
Interchangeable Cavity/Core: Interchangeable cavities and cores allow for flexibility in producing different parts using the same mold base. They can be replaced or swapped out to accommodate various part designs.
Replaceable Cavities and Cores: These are cavities and cores that can be easily replaced or interchanged in the mold. They are used when different part variations or designs need to be produced using the same mold base.
Sliding Cavities and Cores: Sliding cavities and cores have the ability to move or slide within the mold to create complex part features, such as side holes or threads. They are often used for producing parts with internal threads, sliding mechanisms, or other intricate features.
Insert Cavities and Cores: Insert molding involves placing pre-formed inserts or components into the mold, and the cavities and cores are designed to securely hold and encapsulate these inserts during the molding process.
3. Collapsible Core:
This type of core is used for producing parts with intricate internal features or threads. It allows for the creation of hollow or collapsible sections within the molded part.
4. Unscrewing Cavity/Core:
Unscrewing cavities and cores are utilized for producing threaded or screw-type parts. They can rotate or unscrew to release the threaded part from the mold.
The specific types of cavities and cores within each category can vary depending on the complexity of the part design and the specific requirements of the injection molding process. The choice of cavity and core types is determined by factors such as part geometry, parting line considerations, material flow, and ease of mold assembly and disassembly.
Mold & Tooling Service
Cores vs. Cavity in Injection Molding
In injection molding, cores, and cavities are essential components of the mold, but they differ in their functions and characteristics. Understanding the difference between cavity and core tools can better design molds to get high-quality products. There are main differences of Cores and Cavities in injection molding.
1. Function of Core and Cavity in Injection Molding
Cores: Cores are used to create the internal features and intricate details of the molded part. They shape the inner cavities, holes, and complex geometries.
Cavities: Cavities, on the other hand, define the outer shape and surface of the part. They determine the final appearance, texture, and finish.
2. Importance of Core and Cavity in Injection Molding:
Cores: Cores are critical for the functionality and structural integrity of the part. They contribute to its performance and functionality.
Cavities: Cavities primarily influence the aesthetics and visual appeal of the part. They are responsible for the surface quality and overall appearance.
3. Design of Core and Cavity in Injection Molding:
Cores: Core design involves considerations such as part ejection, cooling, and dimensional stability. Complex core designs may include features like slides, lifters, or collapsible cores to accommodate undercuts and facilitate part release.
Cavities: Cavity design focuses on achieving optimal part fill, cooling, and venting. It includes considerations for gating systems, surface textures, and cooling channels to ensure proper material flow, solidification, and desired surface finishes.
4. Location of Core and Cavity in Injection Molding:
Cores: Cores are typically positioned inside the mold to form the internal features of the part.
Cavities: Cavities are located opposite the cores and shape the outer surface of the part.
Conclusion
Cores and cavities are fundamental components in injection molding, each playing a crucial role in the production of high-quality parts. Cores shape the internal features, ensuring functionality, while cavities define the outer appearance, enhancing aesthetics. Their designs, locations, and functions must be carefully considered in mold design to achieve precise and consistent results.
Understanding the importance and characteristics of cores and cavities is essential for successful injection molding processes and achieving desired part specifications.