Proper injection mold maintenance not only extends their service life but also ensures consistent product quality and reduces costly downtime. Both basic and advanced maintenance approaches play a vital, complementary role in this process: basic maintenance prevents frequent problems and keeps molds running smoothly day-to-day, while advanced maintenance addresses deeper issues and further enhances mold longevity. This article explores the importance of mold maintenance, offers practical preventive tips, outlines essential maintenance steps, and distinguishes between basic and advanced strategies to ensure optimal performance.
Why Injection Mold Maintenance Matters
Injection molds are the heart of the plastic manufacturing process. These complex tools shape molten plastic into precise components, and any degradation in mold condition directly affects product quality and production efficiency. Here are the key reasons why injection mold maintenance is critical:
- Extended Injection Mold Lifespan: Regular plastic mold maintenance protects against wear, corrosion, and damage, significantly prolonging the mold’s operational life. This reduces the frequency and cost of replacements.
- Consistent Product Quality: A well-maintained mold ensures precise dimensions and smooth surfaces, eliminating defects like burrs, bubbles, or surface imperfections.
- Minimized Downtime: Unexpected mold failures can halt production. Injection mold preventive maintenance identifies potential issues early, keeping production lines running smoothly.
- Cost Efficiency: By preventing defects and extending mold life, maintenance reduces scrap rates and replacement costs, directly boosting profitability.
- Enhanced Safety: Worn or misaligned components, such as ejector pins, can pose safety risks to operators. Routine injection mold maintenance ensures a safer working environment by addressing these hazards proactively.
At Zhongde, we view plastic mold maintenance as a proactive strategy that safeguards both our equipment and our reputation for delivering high-quality products.
Preventive Injection Mold Maintenance
Preventive injection mold maintenance refers to a planned, systematic set of cleaning, inspection, and servicing activities performed regularly before molds develop noticeable failures or production issues. The primary goal is to prevent problems rather than react to them after they occur. Preventive maintenance for injection molds typically includes several key practices:
Lubrication of Moving Components
Guide pins, bushings, slides, and ejector systems are regularly lubricated with appropriate greases or oils to reduce friction, minimize wear, and keep all moving parts functioning smoothly.
Wear and Damage Checks
Critical mold components such as cavities and cores are periodically evaluated for early signs of wear, cracking, or pitting, enabling timely repairs before minor damage escalates into serious failures.
Maintaining Cooling Efficiency
Cooling circuits are flushed or descaled to eliminate mineral deposits and blockages, ensuring effective heat transfer and preventing warpage or dimensional inconsistencies in molded parts.
Essential Mold Maintenance Steps
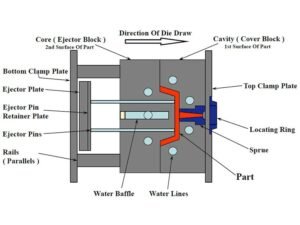
Effective injection mold maintenance requires a clear understanding of the mold’s components and a structured approach to upkeep. Below, we outline the common components of an injection mold and the steps for maintaining them.
Common Mold Components
Cavity and Core: The hollow and solid parts that shape the plastic, requiring regular cleaning to maintain surface quality.
Guide Pins and Bushings: Ensure precise alignment of mold halves.
Ejector Pins: Mechanisms that push the finished part out of the mold, needing lubrication to prevent sticking or wear.
Sprue Bushing: This channels molten plastic into the mold, requiring inspection to prevent blockages.
Cooling Channels: Internal passages for temperature regulation, and must be kept free of debris.
Slides and Lifters: Moving parts that form undercuts or complex shapes.
Injection Mold Maintenance Steps
Basic plastic mold maintenance focuses on routine tasks to keep molds operational. These steps are typically performed daily or per shift:
- Cleaning: Remove all plastic residues and contaminants from mold surfaces and cavities using non-abrasive methods such as ultrasonic cleaning or appropriate solvents.
- Inspection: Examine the mold for wear, corrosion, cracks, or damage. Pay special attention to vents and cooling channels.
- Lubrication: Apply manufacturer-approved lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and prevent seizing.
- Polishing: Lightly polish mold surfaces to maintain smooth finishes on molded parts.
- Component Replacement: Promptly repair or replace worn or damaged parts like ejector pins or springs.
- Temperature System Check: Verify the cooling and heating systems function properly.
- Storage: When molds are not in use, store them in a dry, temperature-controlled environment with protective coatings applied to prevent rust.
- Record Keeping: Document all maintenance activities for future reference and planning.
Basic vs. Advanced Injection Mold Maintenance
Injection mold maintenance can be categorized into basic and advanced mold maintenance. Both levels are complementary. Basic maintenance prevents frequent problems and keeps molds running smoothly day-to-day, while advanced maintenance addresses deeper issues and enhances mold longevity.
The normal type is basic maintenance. This includes daily or routine tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, visual inspections, and minor repairs. Basic maintenance is typically performed by machine operators or maintenance staff and focuses on preventing common issues like rust, residue buildup, and minor wear.
The other level is advanced maintenance. This involves more detailed procedures such as dimensional inspections, non-destructive testing for internal defects, thorough cleaning of complex cooling systems, heat treatment, and precision repairs. Advanced maintenance is usually conducted by specialized technicians and may require disassembling the mold. It aims to restore mold performance, optimize cycle times, and significantly extend mold life, ultimately supporting reliable mold manufacturing quality over the long term.

Conclusion
Injection mold maintenance is a critical discipline that underpins the success of injection molding operations. Investing in plastic mold maintenance is not just about preserving equipment—it’s essential for high-quality injection mold and tooling production and manufacturing excellence in injection molded parts. Through practical injection mold preventive maintenance tips, structured maintenance steps, and a balanced approach to basic and advanced care, Zhongde maintain molds with precision and professionalism to acheieve high precision injection molding service.



