Explore the world of mold surface texture in injection molding, where the visual and tactile qualities of a part are meticulously crafted. This post explores the standard of surface texture. Discover how to choose a suitable injection molding manufacturer and surface finish and the common methods for applying textures to injection molding tools. delve into the art of surface texture and learn how it elevates the quality and appeal of injection-molded products.
What is the Surface Texture In Injection Mold?
Surface texture in injection molding refers to the specific characteristics and qualities of the mold surface that are intentionally designed to influence the appearance, feel, and functionality of the molded plastic parts. Mold surface textures are created through various techniques to achieve desired finishes such as smooth, glossy, matte, textured, or patterned surfaces. These surface textures play a crucial role in enhancing product aesthetics, improving grip or slip resistance, facilitating part release from the mold, and even hiding imperfections.
Texture Application
Texture in injection molding involves the deliberate addition of patterns, textures, or surface treatments to the mold cavity to achieve specific surface finishes on the molded plastic parts. Texture applications in injection molding are used in various industries and for a wide range of products. Here are some examples:
- Automotive industry: Textured surfaces are commonly applied to automotive interior and exterior components such as dashboard panels, door handles, instrument clusters, and steering wheels. These textures enhance aesthetics, provide better grip, and improve the overall quality and feel of the parts.
- Consumer electronics: Textured surfaces can be found on products like mobile phone casings, laptop covers, remote controls, and audio equipment. The textures not only add visual interest but also improve grip and tactile feedback for a better user experience.
- Home appliances: Textured finishes are applied to home appliance components such as refrigerator handles, control panels, and kitchen utensils. The textures enhance usability, provide a premium look, and help mask fingerprints or scratches.
- Medical devices: Textured surfaces are utilized in medical devices to improve grip, facilitate handling, and enhance patient comfort. Examples include textured grips on surgical instruments, textured surfaces on prosthetic devices, and textured handles on medical equipment.
- Packaging industry: Injection molded packaging products, such as containers, caps, and closures, can have various textures to enhance their visual appeal, differentiate brands, and provide ease of handling.
- Industrial and commercial applications: Textured surfaces are used in industrial and commercial products like tools, handles, knobs, and equipment housings to improve grip, provide better ergonomics, and ensure safe handling.
The application of textures in injection molding is versatile and can be tailored to meet specific requirements across different industries and product categories.
Injection Mold Surface Textures Standard
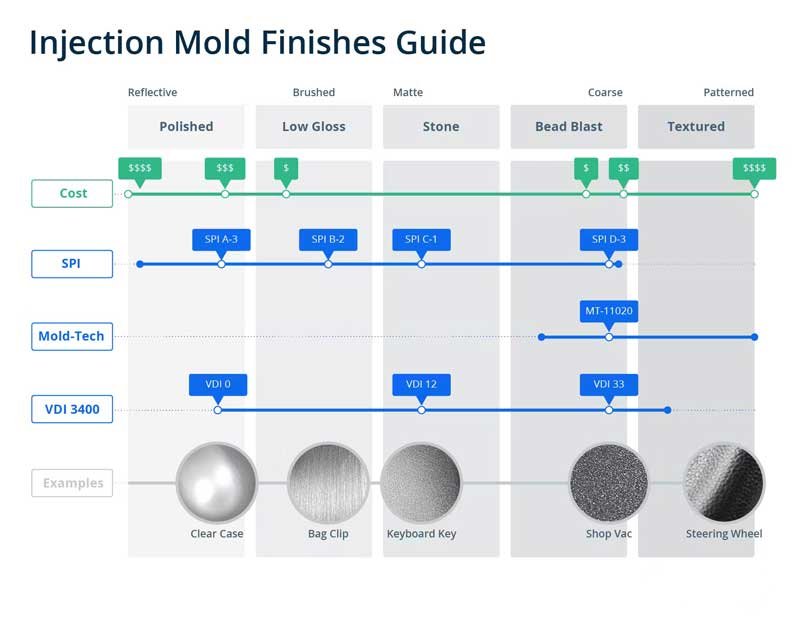
There are industry standards that define the various surface textures used in injection molding. The most widely recognized standard for surface textures is the SPI (Society of Plastics Industry) Mold Finish Guide. Apart from the SPI Mold Finish Guide, there are other industry-specific standards or customer-specific requirements that dictate the desired surface textures for specific applications.
Such as VDI injection moulding surface finish and mold-tech injection moulding surface texture.
It is important for manufacturers and designers to be familiar with these surface texture standards to ensure clear communication, consistent results, and the desired aesthetic and functional properties of their injection molded parts. Here we will introduce those standards in detail.
SPI injection molding surface finish
SPI (Society of Plastics Industry) injection molding surface finish refers to the standardized classification system for mold surface finishes developed by the SPI. The SPI Mold Finish Guide provides a range of surface texture grades and corresponding numerical values and symbols to facilitate clear communication and consistency in surface finish specifications.
The SPI surface finish grades range from high-gloss finishes (Grade A) to rough textures (Grade D). Each grade has specific visual and tactile characteristics, such as glossiness, roughness, and texture uniformity.
- Grade A: This grade represents high-gloss finishes that are smooth and reflective. The surface has a mirror-like appearance with minimal texture or roughness. It provides excellent clarity and glossiness, making it suitable for applications that require a polished and aesthetically pleasing finish.
- Grade B: Grade B finishes have a semi-gloss appearance with slight texture. The surface may have fine lines or marks, but overall, it maintains a smooth and visually appealing finish. It offers a good balance between glossiness and texture, making it suitable for a wide range of consumer products and industrial applications.
- Grade C: This grade represents a moderately textured surface. It exhibits visible texture and can have noticeable variations in glossiness. The texture may be in the form of fine patterns, stippling, or other defined surface patterns. Grade C finishes are commonly used for parts that require some texture or grip, such as handles, grips, and functional components.
- Grade D: Grade D finishes have a rough and textured surface. The texture is more pronounced compared to the other grades, with a noticeable increase in roughness. The surface can have a pebbled or stippled appearance, providing an enhanced grip or hiding surface imperfections. Grade D finishes are often utilized for applications where texture or a non-slip surface is desired, such as tool handles, outdoor equipment, or industrial components.
VDI injection moulding surface finish
The VDI (Verband Deutscher Ingenieure) surface finish standards are identified by numerical codes, with each code representing a specific surface finish. VDI 3400 is a commonly referenced standard that classifies surface finishes based on their appearance and texture. It includes codes such as below:
- VDI 3400-0: This class represents smooth and glossy surface finishes with minimal texture or roughness. It is typically associated with high-quality, polished surfaces that exhibit a mirror-like appearance.
- VDI 3400-12: This class refers to fine stippled surface finishes. The surface has small, closely spaced dots or stippling that create a subtle texture. It provides a visually pleasing finish without being too rough to the touch.
- VDI 3400-30: This class represents coarse stippled surface finishes. The surface has larger, more widely spaced dots or stippling, resulting in a more pronounced texture. It offers a tactile feel and is often used to hide minor imperfections or wear on the part.
- VDI 3400-33: This class refers to orange peel surface finishes. It mimics the texture of an orange peel, characterized by a slightly bumpy surface with small irregularities. This finish is commonly used to reduce the visibility of scratches or imperfections.
- VDI 3400-34: This class represents leather grain surface finishes. It resembles the texture of leather, with a pattern of fine lines or grain marks. It provides a visually interesting and textured appearance.
These are just a few examples of the classifications within the VDI 3400 standard. The standard includes various other classifications with distinct surface textures and appearances, allowing designers and manufacturers to specify the desired surface finish for their injection-molded parts accurately.
Mold-Tech injection moulding surface texture
Mold-Tech provides a wide range of injection molding surface textures, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Here are some common classifications of Mold-Tech surface textures:
- MT-11000 Series: These are fine-grained textures with a smooth appearance. They are often used for parts requiring a high-quality finish, such as consumer electronics and medical devices.
- MT-15000 Series: These textures offer a moderate level of graininess and are suitable for a variety of applications, including automotive interior components, household appliances, and industrial equipment.
- MT-30000 Series: These textures feature a medium to coarse grain pattern and are commonly used for outdoor applications, such as automotive exterior parts, power tools, and agricultural equipment.
- MT-60000 Series: This series includes deeper and more pronounced textures, ideal for creating a rugged or natural look. They are commonly applied to off-road vehicle parts, outdoor equipment, and furniture.
- MT-80000 Series: These textures exhibit highly defined and complex patterns, making them suitable for decorative applications and parts requiring a unique visual appeal, such as consumer goods and luxury products.
Common Methods For Applying Textures To Injection Molding Tools
There are several common methods for applying textures to injection molding tools to achieve the desired surface finishes. It’s worth noting that the choice of texture application method depends on factors such as the desired texture complexity, precision requirements, production volume, and the material being molded. Each method has its own advantages and considerations in terms of cost, lead time, and feasibility.
Mold Texture Made By Polishing
This method involves using polishing tools and abrasives to gradually remove material from the mold surface, resulting in a smooth and glossy texture. It is commonly used for achieving high-gloss finishes or mirror-like surfaces.
Mold Texture Made By Sandpaper
Sandpaper is used to manually sand the mold surface, creating a texture with a fine, uniform pattern. The coarseness of the sandpaper determines the level of roughness or smoothness of the resulting texture.
Mold Texture Made By Grit Stone
Grit stones, such as silicon carbide or diamond stones, are used to manually grind the mold surface, creating a textured pattern. The type and coarseness of the grit stone determine the texture’s characteristics, including its depth and pattern.
Mold Texture Made By Blasting
Abrasive blasting methods, such as sandblasting or bead blasting, involve propelling abrasive particles at high speed onto the mold surface. This process creates a textured pattern by etching or removing material from the surface.
Mold Texture Made By EDM
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) utilizes electrical discharges to erode the mold surface and create a precise texture. This method is often used for intricate or complex patterns that are challenging to achieve through other techniques.
Mold Texture Made By Satin
Satin finishes are achieved by applying a soft, non-abrasive material, such as a cloth or pad, to the mold surface. The material is rubbed against the surface in a consistent manner to create a smooth, lustrous texture.
Factors Influencing Injection Mold Texture Selection
How to choose a suitable injection molding surface? It involves considering several factors that can influence the texture selection. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Part Design and Function: The design and function of the molded part play a significant role in texture selection. Consider the part’s intended use, aesthetics, and functional requirements to determine the appropriate surface finish.
- Material Compatibility: Different materials may react differently to specific textures. Consider the compatibility of the chosen material with the desired texture to ensure proper adhesion, release properties, and overall part quality.
- Aesthetics and Branding: The desired visual appearance and branding requirements of the final product should be considered. Some textures may enhance the product’s visual appeal or align with the brand’s image.
- Functionality and Performance: Certain textures may affect the functional aspects of the part, such as grip, friction, or wear resistance. Evaluate the required functionality and performance characteristics of the part to select a texture that aligns with those requirements.
- Production Volume and Cost: The production volume and cost considerations are essential in texture selection. Some textures may require more complex and time-consuming processes, increasing production costs. Consider the production volume and budgetary constraints to determine the most suitable texture option.
- Mold Complexity and Maintenance: Some textures may require more intricate mold designs or frequent maintenance. Evaluate the complexity and maintenance requirements of the mold to ensure that the chosen texture is feasible and sustainable in the long run.
- Regulatory and Industry Standards: Certain industries or applications may have specific regulatory or industry standards that dictate the acceptable surface finish. Ensure compliance with any applicable standards or regulations when selecting the texture.
Conclusion
Achieving the desired surface texture in injection molding is essential for enhancing the appearance and functionality of molded parts. The selection of an appropriate mold surface texture depends on various factors. By considering these factors and understanding the options available, such as SPI, VDI, and Mold-Tech, manufacturers can make informed decisions to achieve the desired mold surface texture. The right choice of texture can significantly impact the overall quality and success of injection molded parts, ensuring they meet the desired visual and tactile requirements for a wide range of applications.