Injection molding cycle time plays a pivotal role in plastic manufacturing as it directly impacts production efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the highly competitive manufacturing industry. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of injection molding cycle time, including cooling time, and explore how understanding and optimizing this essential factor can lead to increased productivity and streamlined operations for manufacturers. So, let’s embark on a journey to injection molding cycle time and discover how it can revolutionize your plastic manufacturing processes.
What is the Injection Molding Cycle Time?
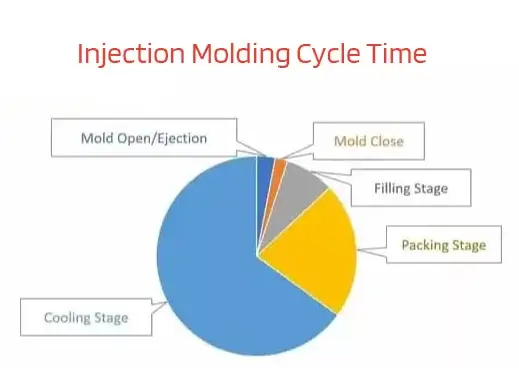
The cycle time in injection molding refers to the total time required to complete one full cycle of the injection molding process. This cycle starts when the molten material is injected into the mold cavity and ends when the finished part is ejected from the mold. The cycle time comprises various stages.
Injection Molding Cycle Time Stages
Injection Time: This is the duration it takes to inject the molten material into the mold cavity until it is completely filled. The injection time is influenced by factors such as the material’s flow characteristics, injection speed, and part geometry.
- Cooling Time: Once the mold cavity is filled with molten plastic, the material needs time to cool and solidify. The cooling time is a critical part of the cycle as it affects the part’s dimensional stability and quality. The cooling time is influenced by the type of material used, the thickness of the part, and the efficiency of the mold cooling system.
- Dwelling Time: After the cooling phase, there is a dwelling time during which the material remains in the mold to ensure it solidifies fully and reduces the risk of warping or distortion.
- Ejection Time: Once the cooling and dwelling stages are complete, the finished part is ejected from the mold using ejector pins or other mechanisms. The ejection time is the duration required to remove the part from the mold.
- Mold Opening/Closing Time: The time it takes to open and close the mold between cycles is also part of the overall cycle time. This time can vary based on the complexity and size of the mold.
The sum of these individual stages forms the complete injection molding cycle time. Reducing the cycle time can lead to increased productivity, higher production output, and cost savings for manufacturers. Therefore, understanding and optimizing the cycle time is crucial for achieving efficient and cost-effective plastic manufacturing processes.
Zhongde Injection Molding Service
How to Calculate Cycle Time in Injection Molding?
Calculating the cycle time in injection molding involves considering the duration of each stage in the molding process. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the cycle time:
Injection Time
The injection time is the duration required to fill the mold cavity with molten plastic. It depends on the material flow rate, injection speed, and the volume of material needed to fill the mold. This time can be obtained from the injection molding machine settings or recorded during production.
Cooling Time
Cooling time is the period required for the molten plastic to cool and solidify inside the mold. The cooling time depends on the material type, part design, and the effectiveness of the mold cooling system. It can be determined experimentally or simulated using mold flow analysis software.
Dwelling Time
Dwelling time is the additional time the material is allowed to stay in the mold after the cooling phase to ensure complete solidification. It is typically a short duration and can be predetermined based on material and part requirements.
Ejection Time
Ejection time refers to the duration taken to remove the finished part from the mold. It is influenced by factors such as part geometry, ejection mechanism, and ejection system efficiency.
Mold Opening/Closing Time
The time taken to open and close the mold between cycles is part of the overall cycle time. This time is influenced by the complexity and size of the mold and the capabilities of the molding machine.
After obtaining the duration of each stage, you can calculate the cycle time using the following formula:
Injection Molding Cycle Time = Injection Time + Cooling Time + Dwelling Time + Ejection Time + Mold Opening/Closing Time
By summing up the time spent in each stage, you will get the total cycle time required for one complete injection molding cycle. It is essential to accurately measure or estimate the duration of each stage to optimize the overall cycle time and enhance production efficiency. Additionally, there are online injection molding cycle time calculators and simulation software available that can help estimate cycle times based on input parameters and optimize the process.
What Are the Factors That Affect the Injection Molding Cycle Time?
Many factors affect the cycle time of injection molding. We can roughly analyze it from four aspects, that is, mold design parameters, product design parameters, injection molding process parameters, and selected materials. The details as below.
Mold Design Parameters
- Cooling System Design: Efficient cooling channels and proper placement in the mold design can significantly impact the cooling time and, consequently, the cycle time. Uniform cooling helps achieve shorter cycle times.
- Runner and Gate Design: Properly designed runners and gates ensure smooth material flow and minimize pressure drop, which can reduce the filling time and improve cycle time.
- Number of Cavities: The number of cavities in the mold affects the number of parts produced in each cycle. More cavities can increase production output per cycle but may require longer cooling times.
Part Design Parameters
- Wall Thickness: Uniform wall thickness promotes even cooling and reduces the potential for warping or sink marks, leading to a more consistent cooling time and cycle time.
- Part Geometry: Complex part geometries with thin sections or intricate features may require longer cooling times, impacting the overall cycle time.
Materials Selection
- Material Melt and Cooling Characteristics: Different materials have varying melt temperatures and cooling rates, affecting the overall cycle time. High-temperature materials may require longer cooling times to solidify properly.
Here is the table for general materials cooling time (seconds) for different thicknesses.
| Materials | Material Thickness 1mm | Material Thickness 2mm | Material Thickness 3mm | Material Thickness 4mm | Material Thickness 5mm | Material Thickness 6mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 1.8 | 7 | 15.8 | 28.2 | 44.0 | 63.4 |
| PA6 | 1.5 | 5.8 | 13.1 | 23.2 | 36.3 | 52.2 |
| PA66 | 1.6 | 6.4 | 14.4 | 25.6 | 40.0 | 57.6 |
| PC | 2.1 | 8.2 | 18.5 | 32.8 | 51.5 | 74.2 |
| HDPE | 2.9 | 11.6 | 26.1 | 46.4 | 72.5 | 104.4 |
| LDPE | 3.2 | 12.6 | 28.4 | 50.1 | 79.0 | 113.8 |
| PMMA | 2.3 | 9.0 | 20.3 | 36.2 | 56.5 | 81.4 |
| POM | 1.9 | 7.7 | 20.3 | 30.7 | 48.0 | 69.2 |
| PP | 2.5 | 9.9 | 22.3 | 39.5 | 61.8 | 88.9 |
| PS | 1.3 | 5.4 | 12.1 | 21.4 | 33.5 | 48.4 |
Note: The above-calculated value is the time required for the material to cool to the mold temperature, but in many instances, this is the time for the material to cool to the deformation resistance temperature. And this time is to determine that the injection molded parts can be ejected without deformation. Therefore, the above values can be understood as the maximum value.
Injection Molding Process Parameters
- Injection Speed and Pressure: Higher injection speeds and pressures can reduce filling time but may increase cooling time due to thicker part sections.
- Melt Temperature: Melt temperature influences material flow and cooling rates, affecting the cycle time.
- Mold Temperature: Properly controlling the mold temperature helps achieve efficient cooling and shorter cycle times.
- Holding Time and Pressure: Optimizing the holding time and pressure ensures complete filling and packing of the part, affecting the overall cycle time.
How to Reduce Injection Molding Cycle Time?
As we know the injection molding cycle time is the sum of all the stages. they are injection time, cooling time, dwelling time, ejection time, and mold opening/closing time. So optimizing each stage can contribute to an overall reduction in cycle time.
Injection Time
- Use High-Speed Injection: Utilize high-speed injection to fill the mold quickly, reducing the injection time.
- Optimize Injection Pressure: Set the injection pressure at the minimum required to achieve proper part filling, avoiding unnecessary pressure build-up.
Cooling Time
- Optimize Cooling System Design: Ensure efficient cooling channel placement and uniform cooling to minimize cooling time.
- Use Mold Temperature Control: Precisely control the mold temperature to achieve optimal cooling rates for the specific material, expediting solidification.
What is cooling time? Read our previous blog: A Comprehensive Overview of Injection Molding Cooling Time
Dwelling Time
- Minimize Holding Time and Pressure: Optimize the holding time and pressure to the minimum required for proper part packing and reduce dwelling time.
Ejection Time
- Implement Fast Ejection Mechanisms: Use fast ejection systems to reduce the time taken for part ejection.
- Proper Ejection Force: Ensure sufficient ejection force to avoid part sticking or damage during ejection.
Mold Opening/Closing Time
- Fast Clamping System: Invest in injection molding machines with fast clamping systems to minimize mold opening and closing time.
- Smooth Mold Movement: Regularly maintain and lubricate mold components to ensure smooth and efficient mold movement.
Conclusion
Calculating injection molding cycle time can improve the plastic injection molding process. Focus on each stage of the injection molding process and choose appropriate strategies, manufacturers can reduce the cycle time and increase production efficiency. Zhongde as an experienced China custom injection molding manufacturer, we are committed to the timely and efficient completion of customer requirements.