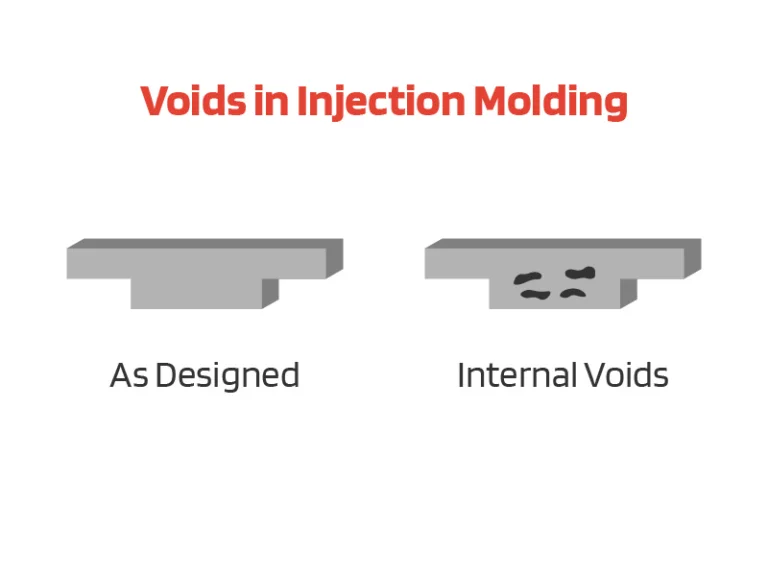
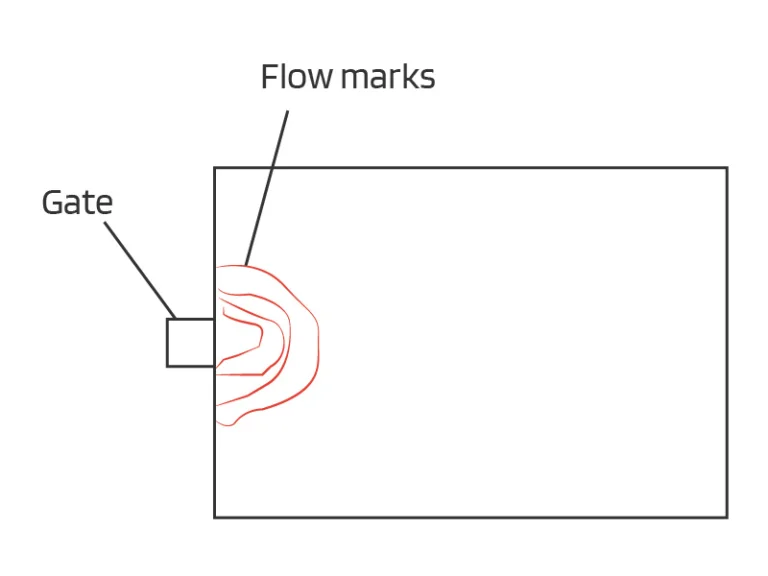
There are countless components made out of plastic using the process of injection molding, and these components are used regularly in multiple industries.
However, the process of injection molding is extremely simple and has no underlying problems, but one of the major issues is the shrinkage of parts.
Yes, after cooling down, these parts shrink and hence lead to a difference from expectations. If you are also learning about this problem of injection molding shrinkage, you are at the right place; read this guide below.
What is Injection Molding Shrinkage?
In the injection molding process, the molten plastic is poured into the cavity and left for solidification. When the component cools down, it turns solid and shrinks in size.
Changes in temperature cause this shrinkage, and there are many other reasons on which this shrinkage may depend.
Shrinkage may take place in two ways, either it is a volumetric shrinkage that takes place when the volume of the part is reduced. On the other hand, linear shrinkage may also take place, and this occurs when the length, width, or height of the component has shrunk.
Causes of Injection Molding Shrinkage
Many factors lead to the shrinkage of injection molded components; some of these factors are as follows:
Properties of Material
Every material has different properties, and usually, when the plastics are molten, they do solidify, and their polymer chains tend to contract, leading to shrinkage.
Every plastic has its shrinkage rate; some may have a minor shrinkage, and some might have a major one.
Amorphous Plastics
Amorphous plastics comprise materials like polycarbonate, polystyrene, or ABS, and their orientation is such that when they melt, the forces between the plastic molecules expand. When they turn solid, they contract.
Hence when the temperature starts to move towards the cooling side, the size of the plastic component tends to shrink.
Semi-crystalline Plastics
Semi-crystalline plastics are of such nature that upon melting, they usually move along with the flow direction and solidify without relaxing. Hence, the rate of shrinkage in such material is high. They tend to recrystallize, and this is what leads to such high shrinkage.
Fiber-Based Materials
Fibers are used in polymers to ensure the strength of the materials, and hence when they are used with plastic, they usually do not contract, nor do they relax, for example, due to the temperature change. Therefore the shrinkage of the materials that have fibers is significantly compared to the ones that do not.
Thermal Contraction
When the plastic is molten, its temperature is high, but gradually the temperature reduces, and the plastic cools down, leading to solidification.
This process of cooling down makes the molecules of the plastic move close to each other, and hence the dimensions are reduced, causing the component to shrink.
Orientation of the Material Molecules
When the molten plastic is injected into the molds, the flow makes the material experience some forces resulting in molecular orientation. This makes the polymer chains flow in a given direction, and hence upon cooling, these molecules try to get back to their actual direction, which leads to shrinkage.
The layout of the Mold
The mold structure plays a very important role in shrinking the component. Also, the cooling process has an impact; some models are designed so that they do not have appropriate cooling channels and hence cause uneven cooling.
This lack of uniformity in the cooling process due to the mold structure leads to the shrinking of the dimensions of components upon cooling down.
Conditions of Processing
When the process of injection molding is carried out, the conditions prevailing during that process also determine the shrinkage of the component.
These factors may comprise the temperature at which the plastic has melted; the time taken by cooling also impacts the shrinkage. When the melting temperature is high, the shrinkage will also be increased. Also, if the cooling time is prolonged, the material will also contract more than usual.

The solution to Mitigate the Shrinkage of Injection Molded Part
Injection-molded parts can be protected against shrinkage when appropriate steps are taken; even if this shrinkage is not eliminated, it could be reduced at least.
- Choosing a material with a low shrinkage rate is always the best idea. Every material has a different rate of shrinkage, and when the material itself shrinks less, the component will also shrink less, and minimal shrinkage won’t affect the purpose of that component.
- The design of mold should also be focused on to mitigate the chances of shrinkage. The gate placement in the mold cavity should be adequate; venting channels must be there to allow trapped gasses to release.
- The injection molding process should also be incorporated with the appropriate melting temperature, which impacts the shrinkage.
- Control must be exercised when the material is poured into the mold because it helps reduce internal stress and shrinkage.
- The focus shall be incorporated on the cooling method, which should be uniform; therefore, the shrinkage rate will be reduced.
Incorporation of Simulation for Reducing Shrinkage
Simulation software also helps reduce shrinkage and allows engineers to manage the material and mold composition accordingly. This software will give engineers a visual image of the entire process.
Hence using this technique, engineers can assess the expected shrinkage that might take place in a particular component.
Therefore by having an insight into all these details, the engineers can easily optimize the relevant processing conditions and alter mold dimensions to attain optimal results.
Conclusion
It is very difficult to analyze the factors that will impact the shrinkage, and also the idea of the output being optimal is something that is not usually identified in the process. Hence, many issues can be resolved by ensuring that the material is chosen with care and that the mold’s design is adequate.
Moreover, it is essential to keep an eye on the temperature of the processing area and also the cooling mechanisms of the mold. When all these factors are taken care of, the chances of shrinkage also reduce to its minimum; hence, it is ignorable.
Check to learn more common plastic parts defects and solutions.