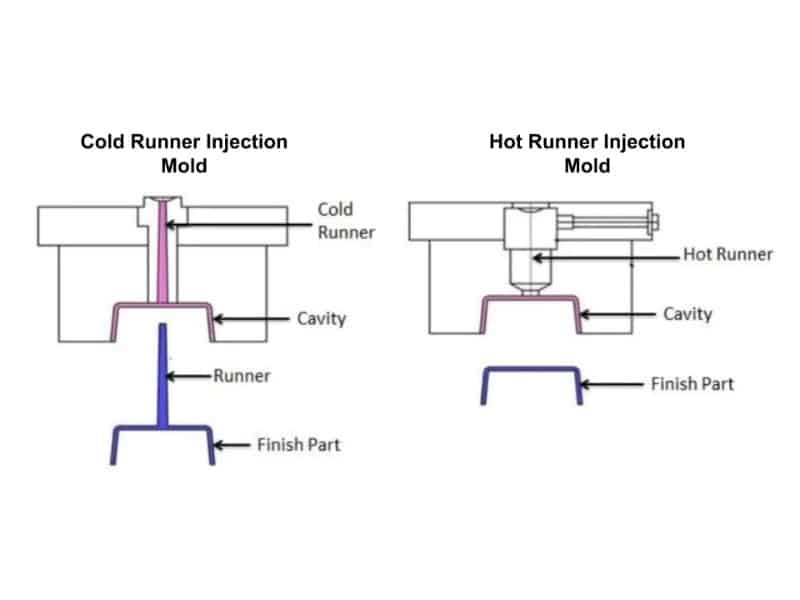
Runner mold systems are the vital pathways that direct molten material into molds, a fundamental component of the injection molding process. In this post, we explore the hot runner and cold runner systems, shedding light on their mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages. Join us and uncover the difference between hot runner and cold runner systems and make informed decisions when it comes to optimizing your injection molding processes.
What is Hot Runner System in Injection Molding?
In the world of injection molding, the hot runner system stands as a precision-engineered solution. Essentially, it’s a network of heated channels and nozzles strategically integrated into the mold. Unlike the cold runner system, the hot runner system keeps the molten material in its liquid state as it flows from the injection unit into the mold cavities.
We’ve written in detail about the hot runner system and its impact on manufacturing before. Please click here to learn more details about the hot runner system.
How Does Hot Runner Mold Work?
Hot runner systems maintain a constant temperature, ensuring that the material remains in a liquid state until it reaches the mold cavity. This is achieved through a series of heated components, including manifold, nozzles, and hot sprue bushings. When the material is injected into the mold, these heated channels prevent it from cooling prematurely, resulting in consistent and precise fills.
Types of Hot Runner System Molds
It’s essential to understand that hot runner molds themselves come in two primary categories:
- Insulated Hot Runner Molds: Insulated hot runner molds minimize heat loss by using insulating materials, ensuring consistent temperature control for precise material flow. It is an ideal choice for heat-sensitive materials and temperature-vulnerable environments.
- Heated Hot Runner Injection Molds: Heated hot runner systems are designed to maintain the plastic melt at a consistent temperature as it flows through the manifold and nozzles, ensuring stable injection molding performance and high-quality parts. These systems typically use either internal heating or external heating configurations, depending on the molding requirements.
Advantages of Hot Runner Systems
Reduced Material Wastage: One of the standout advantages of hot runner systems is the substantial reduction in material wastage. Unlike cold runners, where excess material needs to be discarded after each cycle, hot runners minimize this waste.
Faster Cycle Times: Hot runner systems excel in minimizing cycle times. The consistent temperature ensures that the material flows smoothly and fills the mold rapidly, allowing for faster production.
PS. Click here to learn about other factors that affect cycle time.
Mold Design Flexibility: Hot runner systems allow for more flexibility in gate placement. So hot runner systems provide greater flexibility in mold design. With precise control over material flow, it’s easier to create complex geometries, thin-walled parts, and intricate details in molds.
Optimal Part Quality: Hot runner systems reduce the chances of defects like flow lines, weld lines, or warping, leading to higher-quality finished products.
Applications for Hot Runner Systems Injection Molding
- Thin-Walled Parts: Hot runners are well-suited for producing thin-walled parts, such as those used in the packaging industry.
- Complex Geometries: When molds involve intricate and complex geometries, hot runners shine. They enable the production of parts with challenging shapes and details.
- High-Volume Production: For industries that demand large quantities of identical parts, such as automotive and electronics, hot runner systems are a preferred choice due to their efficiency and speed.
What is Cold Runner System in Injection Molding?
Cold runner systems are a traditional approach to injection molding. They consist of a network of solidified channels, or runners, that guide molten material from the injection unit to the mold cavities. Unlike hot runners, cold runners allow the material to solidify within them between cycles.
How Does Cold Runner Mold Work?
Cold runner systems function by delivering molten material from the injection unit to the mold cavities. Cold runners allow the material to cool and solidify within the runner channels. This solidified material, known as runners, is typically discarded after each cycle. When the mold opens, the runners are ejected, leaving behind the finished parts in the mold cavities.
Types of Cold Runner Systems
Cold runner systems can also be categorized based on the number of mold plates used in their design, Click here to learn the two-plate mold and three-plate mold.
- Two-Plate Cold Runner System: This configuration utilizes two plates: one for the cavity side and one for the core side. The mold opens and closes by moving these two plates apart and together. Two-plate cold runner systems are relatively simple and cost-effective but may have limitations in certain mold designs.
- Three-Plate Cold Runner System: In contrast, three-plate cold runner systems incorporate an additional runner plate. This design allows for more flexibility in gating and can accommodate complex mold designs. However, it typically comes at a slightly higher cost due to the added plate and increased complexity.

Advantages of Cold Runner Systems
- Cost-Sensitive Projects: When minimizing initial investment is a primary concern, cold runner systems are often chosen due to their lower upfront costs.
- Simple Part Geometries: For projects that involve straightforward part designs without intricate details or complex geometries, cold runner systems offer a cost-effective solution.
- Frequent Material Changes: Manufacturers that frequently switch between materials or colors may prefer cold runner systems for their ease of material changeover.
- Low-Volume Production: In cases where production volumes are relatively low, the cost savings of using cold runners can outweigh the material wastage.
Applications of Cold Runner Systems
- Low to Medium Volume Production: Cost-effective for shorter production runs where mold cost and complexity need to be minimized.
- Simple Part Designs: Well-suited for basic geometries that do not require precise flow control or surface perfection.
- Thermoset or Rubber Molding: Common in molding processes where hot runners are not suitable due to material properties.
Differences between Hot Runner and Cold Runner Systems

Through the previous sections, we know the basics of hot runner and cold runner systems. So, what are the key differences between hot runner and cold runner injection molding? We can have a glance at the comparison table of the two runner systems.
| Terms | Hot Runner System | Cold Runner System |
|---|---|---|
| Material Wastage | Minimal wastage due to molten material throughout the process | Material wastage from solidified runners |
| Cycle Time | Faster cycle times | Potentially longer cycle times |
| Mold Design | Allows for complex geometries and precise material control | Simpler mold designs suitable for straightforward parts |
| Part Quality | Minimizes defects like flow lines, weld lines, and warping | Quality parts but may require attention to gate vestiges |
| Production Efficiency | Enhances efficiency with reduced downtime for runner removal | May require more downtime for runner removal and changes |
| Cost Considerations | Higher initial costs | Lower initial costs, but potentially higher material costs |
| Impact on Final Product Quality | Typically results in higher-quality finished parts | Quality parts but may require additional attention to cosmetic issues |
How to Choose The Right Runner Mold System?
Choosing the appropriate runner system in injection molding is a pivotal decision that directly impacts the success of a project. Which runner system is best suitable for your project? Hot runner system or cold runner system? Such as below:
- Material Type: Consider using a hot runner system when working with heat-sensitive materials. Cold runner systems are versatile and suitable for a broad spectrum of materials. They are especially cost-effective for standard materials that do not require precise temperature control.
- Part Geometry: If your project involves complex geometries, intricate details, or thin-walled parts, hot runner systems provide the precision needed to fill these molds uniformly.
- Production Volume: Hot runners are efficient for high-volume production due to their faster cycle times and reduced material wastage. If your project demands a significant number of identical parts, hot runner systems may be the more economical choice in the long run. Cold runner systems are suitable for lower production volumes, as the initial cost savings may outweigh the material wastage in such scenarios.
- Cost Considerations: While hot runner systems have higher initial costs, they may offer cost savings over time through reduced material wastage, cycle time savings, and improved part quality. Cold runner systems are budget-friendly upfront but may incur higher material and operational costs.
Conclusion with Runner Mold System
In the world of custom injection molding service, the choice of a runner system is a pivotal decision that impacts your project’s success.
At Zhongde, we understand the complexities of injection molding and runner system selection. We’re here to offer expert guidance and advice to ensure your projects run smoothly and efficiently. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us for tailored solutions and a deeper understanding of injection molding processes.