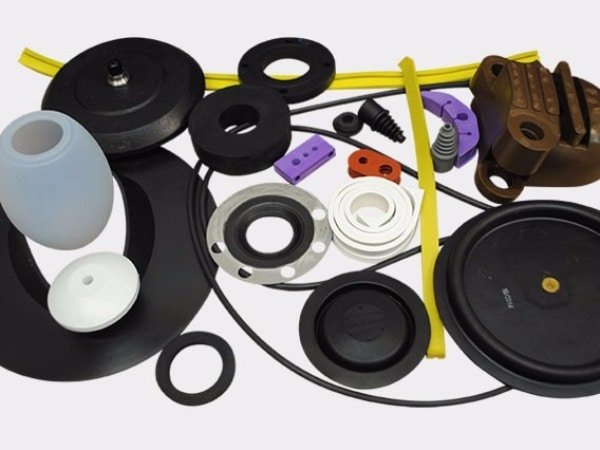
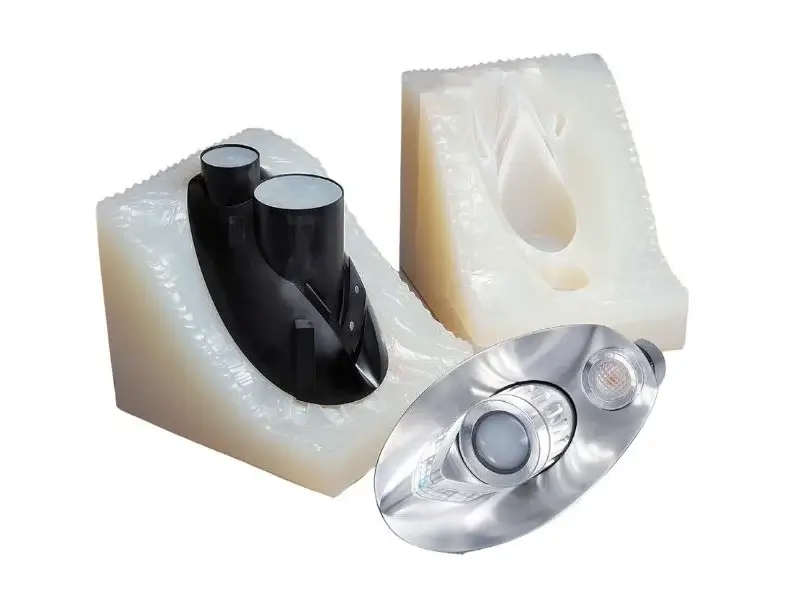
Rubber, a vital material in industrial and daily applications, is categorized into 2 types of rubber: natural rubber (NR) and synthetic rubber. This article delves into the properties of rubber, explores nine common rubber material types, and examines how molded rubber components are produced, highlighting the diversity of different kinds of rubber in practical use.
What is Rubber?
Rubber is a solid material that offers exceptional elasticity and tensile strength, making it highly popular for many different applications with types of rubber molding.
Rubber Characteristics
Rubber material types are distinguished by a unique set of properties that make them indispensable across industries. Below are the key characteristics that define different types of rubber and their versatility.
Exceptional Elasticity: Rubber’s hallmark is its high elasticity. This allows different kinds of rubber to stretch several times their original length and return to their initial shape.
Air Impermeability: Most rubber material types exhibit excellent air impermeability, preventing gas leakage.
Electrical Insulation: Different types of rubber typically offer strong electrical insulation, resisting current flow.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance: Certain different kinds of rubber, especially synthetics, withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -60°C to +350°C. They also resist swelling or degradation when exposed to oils, solvents, acids, and other chemicals.
Durability and Abrasion Resistance: Rubber’s ability to endure abrasion, corrosion, and flex fatigue ensures longevity in dynamic applications. Rubber material types are designed to withstand repeated stress without significant wear.
Main Two Types of Rubber Are There
Natural Rubbers
Natural rubbers are produced naturally by plants and tend to be incredibly soft and wear resistant . They offer excellent elasticity and are useful in many different molds and products.
Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic rubber materials offer excellent tensile strength and also come with the additional benefit of usually being non-allergenic. Accordingly, synthetic rubber materials are commonly used in applications requiring more specific characteristics and in scenarios whereby natural rubber latex causes allergic reactions. Synthetic rubber is made from petrochemicals in laboratory settings.
Nine Common Rubber Materials
The diversity of rubber material types ensures solutions for nearly every industrial need. Below are nine common types of rubber.
1. Natural Rubber (NR)
Natural rubber, derived from polyisoprene, is a staple among rubber material types due to its high elasticity and tensile strength. It excels in tear resistance, electrical insulation, and adhesion to other materials, with solid wear and cold resistance down to -60°C. However, NR struggles against oxygen, ozone, oils, solvents, and acids, and its heat resistance caps at 80°C, making it prone to aging.
Applications:
- Tires, rubber shoes, hoses, and conveyor belts
- Cable insulation and sheaths
- Shock absorbers and engine mounts
2. Silicone Rubber (Si)
Composed of silicon-oxygen chains with organic groups, silicone rubber excels in high and low-temperature resistance (-50°C to +200°C) and ozone resistance. It is food-grade, non-toxic, and electrically insulating. Its drawbacks include lower tensile and tear strength and poor resistance to oils and solvents.
Applications:
- Medical devices and artificial organs
- Drug delivery capsules
- High/low-temperature seals and gaskets
3. Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM)
FKM, a fluorinated elastomer, withstands temperatures up to 300°C and resists acids, oils, and solvents. It offers excellent chemical, ozone, and radiation resistance but is expensive, with poor cold resistance and low elasticity.
Applications:
- Aerospace and automotive seals
- Chemical-resistant hoses and linings
- Defense industry components
4. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
EPDM, a copolymer of ethylene and propylene, excels in ozone, UV, and aging resistance, with a temperature range of -50°C to +150°C. It offers good electrical insulation and chemical stability but has poor self-adhesion and oil resistance.
Applications:
- Automotive seals and hoses
- Electrical cable insulation
- Waterproofing materials and steam hoses
5. Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
NBR, a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, is renowned for excellent oil resistance, with good wear and heat resistance up to 120°C. Higher acrylonitrile content enhances oil resistance but reduces cold resistance (-25°C to +100°C). It has poor electrical insulation.
Applications:
- Oil-resistant seals, gaskets, and hoses
- Rubber rollers and industrial adhesives
- Fuel and oil system components
6. Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
CR, or neoprene, is a chloroprene polymer with good ozone, oil, and chemical resistance. It self-extinguishes when ignited and has better mechanical properties than NR, with a temperature range of -45°C to +100°C. Its drawbacks include poor cold resistance and storage stability.
Applications:
- Cable sheaths and protective covers
- Oil-resistant hoses and chemical linings
- Flame-retardant mining products
7. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
SBR, a copolymer of butadiene and styrene, offers wear and heat resistance similar to NR and is the most produced synthetic rubber. It has good aging resistance but lower elasticity and poor oil and solvent resistance, with a temperature range of -50°C to +100°C.
Applications:
- Tires and conveyor belts
- Rubber shoes and adhesives
- General industrial products
8. Butyl Rubber (IIR)
IIR, a copolymer of isobutylene and isoprene, excels in air impermeability, ozone, and heat resistance up to 130°C. It resists strong acids and has good electrical insulation but has poor elasticity, slow vulcanization, and low oil resistance.
Applications:
- Tire inner tubes and balloons
- Chemical equipment linings
- Heat-resistant conveyor belts
9. Polyurethane Rubber (PU)
PU rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and toughness, with good resistance to oils and chemicals. It performs well in dynamic applications but has limited heat resistance (up to 80°C) and poor hydrolysis resistance.
Applications:
- Conveyor belts and rollers
- Automotive suspension components
- Seals and gaskets for industrial use
Rubber Molding Processes and Components
Molded rubber components are precision parts created through processes like injection molding and compression molding.
Injection molding rubber involves injecting molten rubber into a mold under high pressure, ideal for high-volume, complex shapes like seals and gaskets. Rubber compression molding places rubber into a heated mold, compressing it to form the desired shape, suitable for larger, simpler parts.
Common Rubber Products
Rubber O-rings: Circular seals made from flexible different kinds of rubber, O-rings prevent leakage in mechanical systems like automotive engines, hydraulic systems, and plumbing, forming tight seals under pressure to ensure fluid and gas containment.
Rubber Pipes: Flexible tubes crafted from durable rubber material types, these pipes transport fluids, gases, or materials in industrial processes, agricultural systems, and automotive applications, offering flexibility for dynamic environments.
Rubber Extrusions & Profiles: Custom-shaped through extrusion, these products, made from different types of rubber, serve as automotive weather seals, door seals, and industrial machinery components, providing tight fits and durability.
Rubber Gaskets: Essential for leak prevention, gaskets use different kinds of rubber to seal mating surfaces in engines, pumps, and machinery, resisting chemicals, heat, and pressure for reliable performance.
Rubber Seals: These prevent dust, moisture, or contaminant ingress in automotive, construction, and marine applications, leveraging rubber material types to enhance machinery lifespan.
Rubber Mounts: Designed to reduce vibration and noise, mounts made from different types of rubber are used in vehicles and industrial equipment, providing cushioning and stability.
Rubber Hoses: Flexible tubes from different kinds of rubber transport liquids, gases, or powders in industrial, automotive, and construction settings, valued for durability and chemical resistance.
Rubber Bushings: Used in automotive suspension systems and machinery, bushings from rubber material types reduce vibration and noise, improving comfort and stability.

Conclusion With Type of Rubber Material
The world of rubber material types offers a remarkable range of solutions. These different kinds of rubber enable the production of critical components through advanced molding techniques, ensuring precision and durability across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical. Our factory Zhongde specializes in the production and customization of these high-quality rubber products and rubber material selection, leveraging the diverse properties of different types of rubber to meet your specific requirements. Welcome to contact and tailored solutions.




