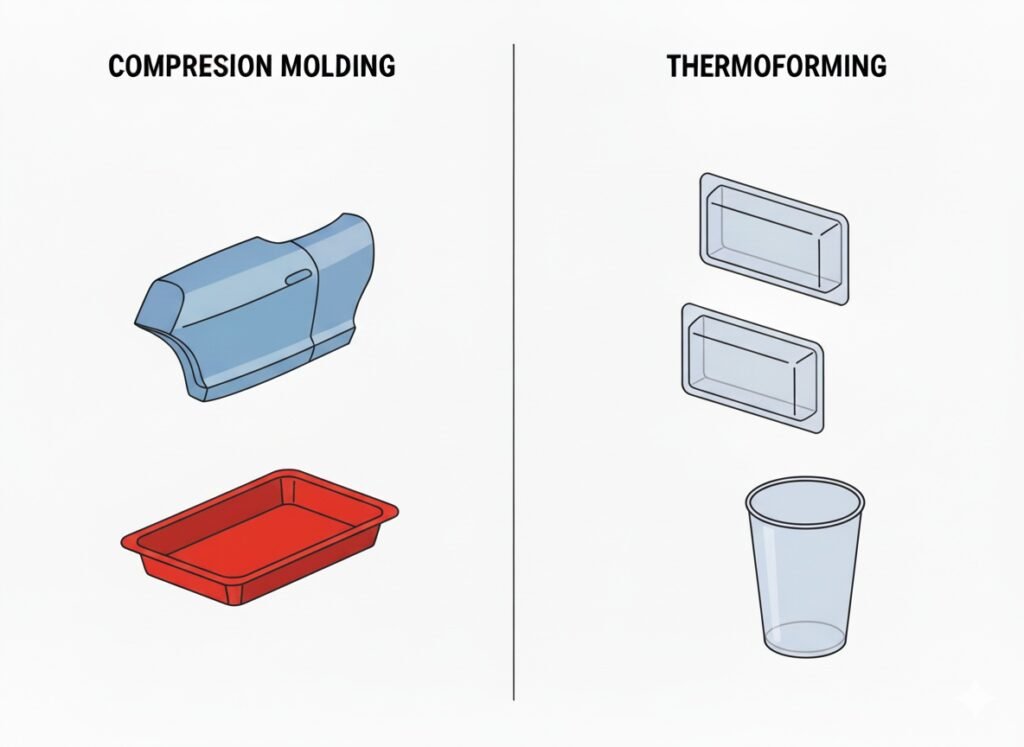
In modern plastic manufacturing, Compression molding and thermoforming share basic principles. Both apply heat to soften plastic and pressure to form it into the desired shape. They work with polymers and support recyclable materials.
What is Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a process in which preheated plastic material or rubber is placed into an open, heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to force the material to conform to the shape of the mold. After a set curing or cooling period, the part is removed, resulting in a finished product.
Materials commonly used in compression molding include thermosetting plastics, engineering resins, rubber and elastomers.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Compression Molding
Compression molding offers several advantages. It can produce parts with high dimensional accuracy and consistent mechanical properties. The method is suitable for thick-walled components and allows the use of high-performance materials. It is also ideal for components that require excellent heat resistance or electrical insulation.
However, there are limitations. The production cycle for compression molding is generally longer than for some other forming methods, and the cost of molds can be significant. It may also be less suitable for high-volume production of thin-walled components, where faster methods like thermoforming could be more efficient.
Applications of Compression Molding
Compression molding product is widely used in industries requiring durable, high-strength components. Examples include:
- Automotive parts: Electrical insulation components, under-the-hood parts, and structural elements.
- Electrical and electronic components: Switch housings, circuit boards, and connectors.
- Household appliances: Handles, knobs, and components.
What is Thermoforming?
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process in which a plastic sheet is heated until pliable, then formed over a mold to create the desired shape using vacuum or pressure. The material is cooled and removed from the mold, resulting in a finished product. This process is widely used for thin-walled parts and products where speed and cost efficiency are priorities.
Materials commonly used in thermoforming include thermoplastic plastics, lightweight sheet materials Emgineering plastics.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermoforming
Thermoforming offers several key benefits. The process is faster than compression molding, making it well-suited for medium to large production runs. Molds are generally less expensive, and it allows flexibility in creating different product sizes and shapes. It is particularly efficient for products that do not require high structural strength or intricate detail.
The disadvantages include lower precision compared to compression molding and limited control over wall thickness. Thin-walled products may experience uneven material distribution, which can affect mechanical properties.

Applications of Thermoforming
Thermoforming is commonly used in applications that require lightweight, cost-effective packaging or components. Examples include:
- Food packaging: Trays, clamshells, and containers designed for easy storage and transport.
- Medical device packaging: Sterile blister packs and protective cases.
- Consumer and household products: Appliance panels, display components, and promotional packaging.
Key Differences Between Compression Molding and Thermoforming
The following table summarizes the main differences between the two processes:
| Feature | Compression Molding | Thermoforming |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermosetting plastics, rubber | Thermoplastic sheets |
| Mechanism | High pressure in closed mold | Vacuum/pressure on sheet |
| Best Scale | Low-to-medium volume, durable parts | High volume, lightweight parts |
| Mold Cost | High | Low |
| Suitable Part Type | Thick-walled, complex, high-strength components | Thin-walled, large-scale, cost-sensitive products |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, electrical, durable household components | Packaging, medical trays, appliance panels |
Which Method is Right for Your Project?
Choosing the appropriate forming method depends on material requirements, part complexity, production volume, and cost considerations. Compression molding is ideal for applications requiring high precision, durability, and structural integrity, whereas thermoforming is more suitable for high-volume, thin-walled products where speed and cost efficiency are critical.
Zhongde, custom molding manufacturer, can assist in evaluating project’s specific requirements and recommend the most suitable method, ensuring that production process is both efficient and cost-effective.