High volume production plays a key role in meeting market demand, reducing costs, and increasing profitability. This article explores what high volume production is.
What is High-Volume Production?

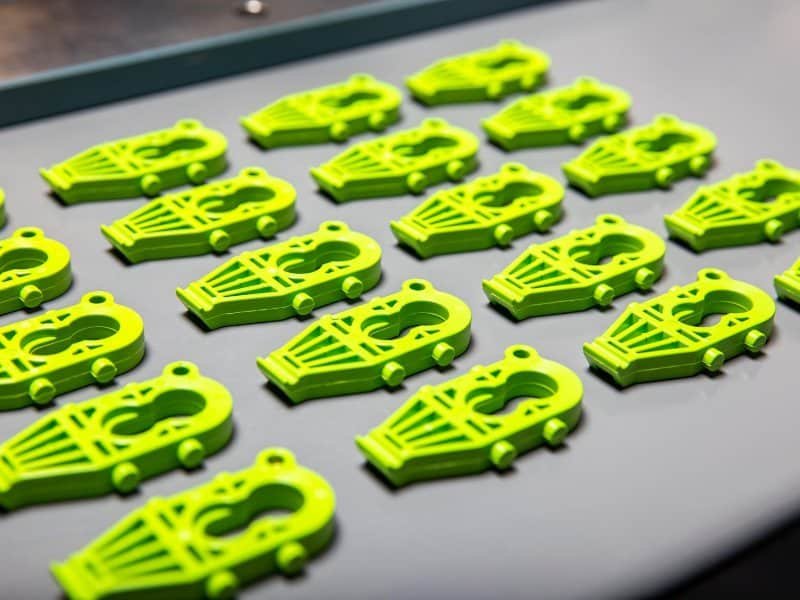
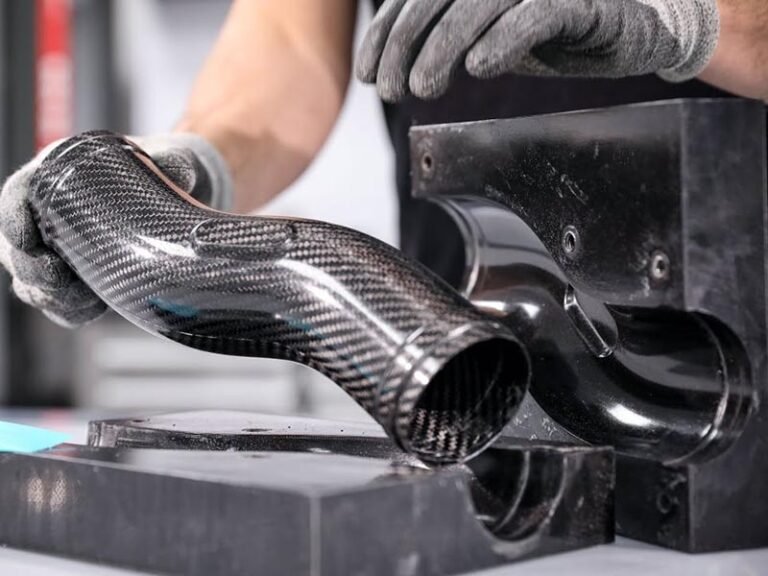
High-volume production, also known as high volume manufacturing (HVM), is the process of producing large quantities of standardized products using automated systems. This approach leverages advanced machinery and streamlined workflows to achieve significant output, often exceeding 10,000 units per day in industries. By integrating automation and precision engineering to achieve economies of scale.
Advantages of High-Volume Manufacturing
High volume production offers numerous benefits that drive its adoption across industries. Below are key advantages.
- Cost Efficiency: Bulk material purchasing and efficient labor allocation reduce overall production expenses and lower unit costs. Additionally, the automation minimizes labor expenses.
- Consistent Quality: Automated machinery and standardized workflows minimize human error, ensuring uniformity and high quality across all units produced.
- Faster Production Speed and Market Entry: Specialized processes and automated lines enable rapid manufacturing cycles. Companies can bring products to market sooner, gaining competitive advantages and establishing stronger brand presence.
- Reliable Supply Chain: High volume production supports stable inventory levels, ensuring timely delivery.
- Increased Sales Capacity: The ability to meet large-scale demand supports market expansion and satisfies retail and wholesale inventory needs effectively.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Lean manufacturing principles and continuous process improvements optimize throughput, reduce waste, and maximize resource utilization.
Disadvantages of High Volume Production
Despite the clear advantages, high volume manufacturing also has some limitations worth considering:
- High Initial Costs: Setting up automated high volume manufacturing processes requires substantial investment in machinery and tooling.
- Limited Flexibility: Changes in product design or customization are difficult and costly once high volume production ramps up.
- Overproduction Risk: Poor demand forecasting can lead to excess inventory, storage costs, and potential waste.
Manufacturing Methods for High-Volume Production
Different manufacturing processes suit high volume production needs. Each method offers unique applications, operational flow, and benefits:
Injection Molding
Injection molding is suitable for producing high volumes of plastic parts such as housings, casings, and containers, and is a core custom injection molding service. Molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Advantages include rapid cycle times, high precision, excellent surface finishes, and scalability for complex designs.
Stamping

Stamping involves pressing metal sheets into desired shapes using dies. It is ideal for metal components like brackets, connectors, and chassis parts. Sheet metal is fed into a stamping press, which cuts and forms parts using a die. This process is fast, cost-effective, and yields consistent part geometry with minimal labor.
Die Casting

Die casting is designed for manufacturing durable metal parts such as engine components or housings. Molten metal is forced under high pressure into precision molds. This process produces strong parts with tight dimensional tolerances and smooth surfaces at high volumes.
Compression Molding

Compression molding is ideal for producing durable rubber and thermoset plastic parts in medium to high volumes. Material is placed into a heated mold cavity, then pressed and cured into the desired shape. This process delivers strong, consistent components and is widely used for automotive seals, gaskets, and structural parts, making it a reliable method for compression-molded products.
CNC Machining

Computer numerical control (CNC) machining uses programmed tools to cut materials. It is suitable for high-precision plastic and metal parts like automotive gears, aerospace fittings, and metal connectors. A computer guides cutting tools to shape raw material into precise parts. Benefits include tight tolerances (within 0.01 mm), versatility across metals and plastics, and consistent quality for high volume manufacturing.
Partner with Zhongde for High Volume Production
Zhongde is good at high volume production by offering advanced mold design and forming capabilities that support efficient large volume manufacturing. The expertise enables the delivery of high-quality, consistent products at scale while also providing customized manufacturing solutions tailored to client needs. As a china custom parts manufacturer, Zhongde welcomes you to contact us for high volume production service and custom molding solutions.
Start A New Project Right Now!
FAQ
Minimum order quantities typically start at 10,000 units, but this can vary depending on the product and manufacturer.
Consistency is maintained through automated processes, strict quality control protocols, real-time monitoring, supplier audits, and regular inspections throughout production.




