Polyvinyl chloride is one of the most versatile and widely used thermoplastics in modern manufacturing. PVC injection molding has become an efficient and precision manufacturing method for various industries. In this article, we will explore the polyvinyl chloride material properties and injeciton molding process.
Overview of PVC Plastic Material

PVC plastic, or polyvinyl chloride, is a thermoplastic polymer synthesized from vinyl chloride monomers (VCM). PVC’s unique properties include chemical resistance, durability, and recyclability, which make PVC plastic highly adaptable for injection molding plastics. PVC’s ability to be tailored with additives like plasticizers, stabilizers, and lubricants. These additives allow PVC material for injection molding to be formulated into two primary forms: rigid and flexible, each serving distinct purposes.
- Rigid PVC (Unplasticized PVC or uPVC): Rigid PVC offers outstanding stiffness and flame retardancy, making it an ideal material for load-bearing applications. It’s widely used in construction for durable components like pipes, window frames, and electrical housings.
- Flexible PVC: By adding plasticizers, PVC transforms into a soft and elastic material with enhanced flexibility. This flexibility makes it suitable for applications such as medical tubing, wire and cable insulation, automotive parts, and other goods requiring pliability and resilience.
Why Injection Molding for PVC
The PVC injection moulding process offers several benefits, making it a good method for manufacturers:
- Versatility: The ability to customize PVC material for injection molding with additives allows for tailored rigidity, flexibility, transparency, and color, meeting diverse application needs.
- Cost-Effective: PVC resin is widely available and economical. Injection molding allows for high-volume manufacturing with low per-unit cost, making it suitable for large-scale production.
- Durability and Chemical Resistance: Parts produced through PVC injection molding resist environmental degradation, chemicals, and physical wear, ensuring longevity.
- Flame Resistance: The chlorine content in PVC enhances safety by making parts inherently flame-retardant, critical for electrical and construction applications.
- Dimensional Stability and Precision: The PVC moulding process enables the creation of complex, high-precision parts with tight tolerances.
- Sustainability: PVC’s recyclability supports eco-friendly production, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Lightweight and Good Color Retention: PVC parts offer a favorable strength-to-weight ratio and maintain color stability over time, ensuring aesthetic and functional longevity.

PVC Injection Molding Service
Polyvinyl Chloride Injection Moulding Process
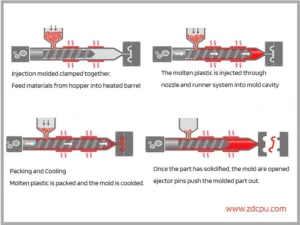
The pvc injection moulding process is a highly controlled manufacturing method tailored to the unique properties of PVC material for injection molding. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the essential steps:
- Material Preparation: PVC material for injection molding begins as pellets or powder. Proper drying is necessary to reduce moisture content below 0.1%.
- Melting and Plasticization: The dried PVC is fed into a heated barrel, where it is melted to a molten state. Additives such as thermal stabilizers and lubricants are incorporated to enhance flow and prevent thermal degradation during the PVC moulding process.
- Injection: The molten PVC is injected under high pressure into a temperature-controlled mold cavity. The mold design includes gates and runners to guide precise flow and filling of the part shape.
- Cooling and Solidification: The mold cools rapidly to solidify the part, locking in its shape and dimensions.
- Ejection and post processing: Once solidified, the mold opens, and the part is ejected into a collection bin. Post-processing, such as trimming or surface finishing, may follow to achieve the desired specifications.
Key Considerations for PVC Injection Molding
To achieve optimal results in PVC injection molding, manufacturers must address several critical factors to prevent defects and ensure part quality:
Temperature Control
PVC is prone to thermal degradation above 200°C. The barrel zones are typically set between 140°C and 180°C, while molds stay cooler to enable rapid solidification.
Mold Design
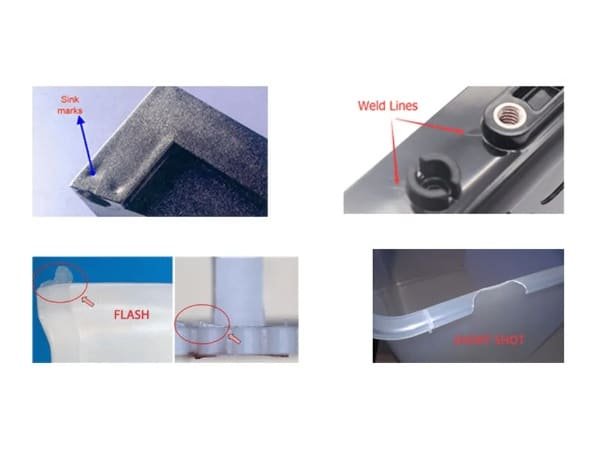
The mold must accommodate uniform wall thickness, gradual transitions (no abrupt thickness changes greater than 10-15%), sufficient draft angles (0.5-1%), and carefully designed gates to ensure proper flow. Cooling channels must be optimized for uniform temperature distribution to avoid warping or sink marks.
Shrinkage Control
PVC’s shrink rate ranges from 0.2% to 0.5%, influenced by hardness, mold temperature, and additives used. Designers should account for this in mold dimensions and optimize process parameters accordingly.
Demolding
Efficient ejection systems combined with mold surface finishes and draft angles help part release without causing defects. Proper lubrication or mold release agents may also be used to facilitate this step.
Drying and Moisture Management
Despite PVC being less hygroscopic than some plastics, drying pellets before melting reduces cosmetic imperfections and internal stresses.
Applications of Injection Molded PVC

The versatility of PVC plastic makes it indispensable across a wide range of industries, with PVC injection molding enabling the production of tailored components:
- Automotive: Interior trims, dashboards, cable insulation, instrument panels, and tubing, connectors and housings.
- Medical Devices: Medical tubing, catheters, blood bags, masks, and other healthcare products
- Construction: Pipes, window and door frames, siding, gutters, and fittings.
- Consumer Goods: Packaging, bottle caps, wire spools, furniture components, and household items.
- Electronics: Enclosures and insulating components.
Choosing Zhongde for PVC Injection Molding
When sourcing a manufacturer for PVC injection molding, reliability and expertise are matter. Whether for rigid PVC components or flexible customized parts, Zhongde’s expertise in minimizing warping, sink marks, and flash support guarantees high quality results. As a trusted provider of injection molding service, Zhongde ensures precision and durability across diverse applications. Contact Zhongde today to get custom PVC injection molding solutions.
Start A New Project Right Now!
FAQ
Common problems include warping (part deformation), flow lines (surface streaks), sink marks (indentations), jetting (uneven flow), air traps (bubbles), short shots (incomplete filling), and brittleness. These issues often arise from improper mold design, insufficient venting, incorrect temperature or pressure settings, and uneven cooling.
Common alternatives to PVC injection molding include high-density polyethylene (HDPE) injection molding, polypropylene (PP) injection molding, and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) injection molding. These materials offer varying benefits in toughness, flexibility, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance.
If the temperature is too high, PVC can degrade, releasing harmful gases and causing defects like burns or discoloration. If too low, the material may not flow properly, leading to incomplete filling, short shots, or weak parts.



