Stamping molds shape metal sheets into precise components for industries like automotive and electronics, delivering efficiency and accuracy. These tools are essential to high-volume metal stamping service, offering consistent quality and scalability. Known as mold stamping or stamping moulds, these tools excel in high-volume production. This guide explores their structure, manufacturing techniques, types, lifespan factors, and how to choose expert manufacturers for reliable metal stamping molds.
What Is a Stamping Mold?
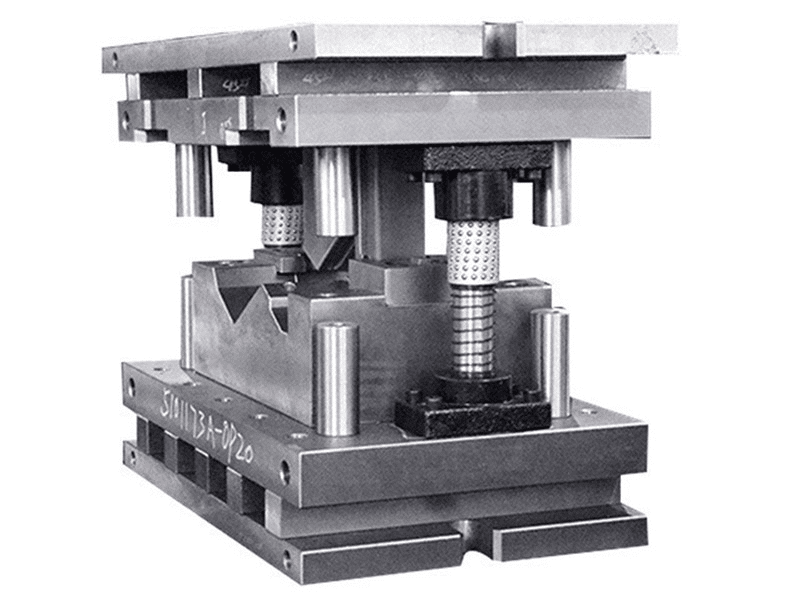
A stamping mold is a specialized tool used in mold stamping processes to shape or cut metal sheets by applying pressure. Unlike injection molds used in plastic manufacturing, stamping molds are designed specifically for cold metal forming operations such as punching, bending, drawing, and forming. The mold applies force to a flat metal blank, causing it to deform plastically or separate, resulting in a part with precise dimensions and properties.
The key difference between a stamping mold and an injection mold lies in the material and process: stamping molds work with metal sheets in cold conditions, while injection molds shape molten plastic.
Structure of Stamping Molds
The stamping mold comprises two primary sections: the upper and lower molds. The upper half mounted on the press ram and the lower half fixed on the press bed. They are working in tandem to shape materials.
The upper mold, often called the punch assembly, includes critical components like the punch holder, punch, stripper plate, and guide bushings. The punch cuts or deforms the metal, while the stripper plate ensures clean separation after each cycle. Guide bushings maintain alignment, preventing defects during high-speed operations.
The lower mold, or die assembly, houses the die, die plate, guide plates, and base. The die shapes the material as the punch presses against it, and guide plates ensure stability. Together, these components form a robust stamping mould capable of withstanding tons of pressure.

The Stamping Mold Process
Manufacturing stamping molds involves advanced techniques to ensure precision and durability in mold stamping:
Digital Design: CAD tools create metal stamping mold blueprints, optimizing designs for performance and minimizing errors.
High-Speed Milling: High-speed milling machines, often equipped with 7-axis capabilities, can operate at spindle speeds ranging from 15,000 to 100,000 revolutions per minute. This results in stamping moulds within 10μm tolerances.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Electrical discharge machining crafts intricate metal stamping mold features such as complex contours, sharp internal corners, and intricate cavities, ensuring complex shapes without undercuts.
Draft Angles: Walls angled at 1–2 degrees ease part ejection, vital for mold stamping efficiency.
Surface Coating Technology: TiN or TiAlN coatings enhance stamping mold durability, reducing wear in processes like deep drawing.
Types of Stamping Molds
Stamping molds vary by function and structure, each tailored to specific manufacturing needs. Understanding these types helps manufacturers select the right stamping mould for their projects. Understanding these types and the corresponding types of stamping process helps manufacturers select the right stamping mould for their projects.
By Function
- Blanking Molds: These metal stamping molds cut flat shapes from metal sheets, producing parts like washers or electronic connectors with clean edges.
- Bending Molds: Used to deform metal into angles, bending stamping moulds create components like brackets or chassis frames.
- Drawing Molds: These molds stretch metal into hollow shapes, such as cups or automotive fuel tanks, requiring precise force control.
- Forming Molds: Focused on local deformation, forming mold stamping creates complex contours without cutting, ideal for decorative panels.
- Composite Molds: Combining multiple operations (e.g., blanking and bending), composite stamping molds streamline production for intricate parts.
By Structure
- Single-Stage Molds: Perform one operation per cycle, suitable for low-volume or custom projects.
- Progressive Molds: Feature sequential stations, completing multiple steps (e.g., cutting, bending) in one pass. Progressive metal stamping molds dominate high-volume production, like automotive parts.
- Composite Molds: Execute combined operations in a single stroke, enhancing efficiency for complex components.
Factors Affecting Stamping Mold Lifespan
The lifespan of stamping molds significantly influences production efficiency and costs, determined by three key aspects:
Design
Effective stamping mold design ensures durability. Balanced process distribution in progressive mold stamping avoids stress concentration, while smooth angles prevent defects like wrinkling. Selecting raw materials with good formability reduces deformation forces, enhancing metal stamping mold longevity.
Mold Production
Quality manufacturing is critical for stamping molds. High-hardness materials, like carbide, boost stamping mould durability, chosen based on component stress. Precise machining minimizes surface roughness, improving wear resistance. Proper heat treatment ensures metal stamping mold strength, while poor processes cause wear or cracking. High-quality castings and forgings prevent defects that could scrap mold stamping tools.
Mold Usage
Proper use and maintenance extend stamping mold life. Accurate, rigid mold stamping equipment prevents strain, while precise guide mechanisms reduce wear. Regular lubrication and inspections eliminate cracks or gaps in stamping moulds. Routine maintenance of moving parts, like wedges or unloaders, ensures reliable performance, minimizing downtime for metal stamping molds.
You Need to Know About Stamping Mold
What is The Effect of Deep Sill In Over Mold?
1. Increase the friction resistance of the feed material, so that the surface of the deep drawing part bears sufficient tensile stress, improve the bending stiffness of the deep drawing part and reduce the concave surface, distortion, slack and wave pattern caused by the resilience;
2. Adjust the fluidity of the material to make the fluidity and frictional resistance of each part of the whole drawing process equal, or make the amount of material injected into the mold suitable for each part of the steel part to avoid the situation of “less wrinkles, less cracks”;
3. Expand the scope of adjustment of the hemming force. On the double-action punching machine, adjusting the height of the four corners of the outer guide rail slider only roughly adjusts the hemming force, and it is not possible to control the ash input of each part to meet the needs of the steel parts. Therefore, it must rely on the hemming surface And drawbeads to assist in manipulating the working pressure of each part;
4. When there are drawing ribs, there are regulations that will reduce the surface roughness of the production and processing of the edging noodles, which reduces the difficulty coefficient of manufacturing the drawing dies for large and medium-sized covering parts; in addition. Because of the presence of the deep-drawing ribs, the gap between the upper and diastolic edge pressing surfaces is increased, so that the damage of the edge-bound noodles is reduced and the service life of the mold is improved;
5. Correct the shortcomings of uneven material and eliminate the probability of causing loads. Because when the material is injected into the cavity after fluctuating according to the drawing bead, it is equal to the effect of rolling straightening.
How Are Process Incisions Formed in Cold Stamping?
1. Break through this type of method during blanking. It is used to partially form deep and shallow places.
2. This technique takes advantage of the initial radial stretching of the material. After partial deformation, process incisions are torn (not completely separated) and the remaining scrap is removed in subsequent operations.
What is the layout standard of craft incision?
The size and appearance of the process incision depends on the conditions of the area where it is located and the regulations of its outward filling materials. Generally, the following standards are required:
1. The cut should be consistent with the part of the protruding contour, so that the material flows reasonably.
2. Sufficient dipping edge should be left in the middle of the incision to make the mold base tighten the material to ensure clear molding and prevent the shortcomings such as wavy lines, so as to ensure that excellent quality of the opposite edge hole edge can be obtained after trimming.
3. The cut part of the incision (that is, the opening) should be adjacent to the edge of the raised position, or an area that is very easy to split.
4. The total number of cuts should ensure that the deformation of each part of the protruding position tends to be even, otherwise the pattern may not be avoided. As shown in the figure below, the original design can only have two process cuts on the left and right. As a result, cracks are still caused in the middle. Afterward, the cut in the middle (dashed line) is added to completely eliminate the cracks.
In what stamping die manufacturing must choose high-precision progressive die?
In the manufacture of a large number of stamping dies, large, medium and small stamping parts with thinner materials and higher precision must be used with multi-station high-precision progressive dies. For large precision metal stamping parts, it is suitable for stamping parts processing of multi-station conveying molds.
What are the regulations for wearing parts in high-precision molds?
The structure of high-precision molds is cumbersome, the production technology standards are high, and the cost is relatively high. In order to ensure that the entire mold has a higher service life, it is very stipulated that the mold parts are quickly, conveniently, and reliably replaced after the mold parts are destroyed or damaged. Therefore, it is stipulated that the key parts of the mold have tolerance matching, and such mold parts have exchange characteristics of stamping dies. It can be called a tolerance die.
What is the practical significance of the layout design of high-precision progressive die?
The effective layout design plan can coordinate the production and processing of each station of the mold, can further improve the utilization rate of materials, production precision, production efficiency and mold life, and can also reduce the difficulty of mold production. Therefore, the layout design plan is the most important comprehensive technical problem in the high-precision progressive die design plan. The orientation of the stamping die, the frequency of the shape frequency and the relative deformation level, the probability of the mold structure and the production and processing technology must be determined. Only by carrying out comprehensive and specific analysis can the layout tend to be effective.
What is a plasmid vector?
In the progressive die work, the blocks that transport the blanks to various stations for various cold stamping and forming production processes are called plasmid carriers. The part where the plasmid carrier and the blank are connected is called the edge, and the part where the blank and the blank are connected is called the overlap. During work, it is stipulated that the plasmid vector should be continuously fed in a stable and precise position during the dynamic production and processing, so that the plasmid vector has a certain compressive strength.
What are the requirements for the mold base for high-precision progressive molds?
M high-precision progressive die stipulates that the die has high compressive strength, good rigidity and high precision. Therefore, alloy structural steel is generally used as the mold base, and its thickness is thicker than the standard mold base. The lower mold base is 5-10mm thick, and the upper mold base is 10-15mm thick.
Selecting Professional Stamping Mold Manufacturers
To source reliable stamping molds, choose manufacturers skilled in mold stamping. They should offer precision stamping moulds using CNC machining, tailored to your needs. Quality certifications ensure consistent metal stamping mold performance. Look for ongoing support to extend stamping mold life.
Zhongde, a trusted leader in stamping mold manufacturing, offers precision-engineered solutions and dedicated services. Contact Zhongde to power your production with top-tier stamping moulds.