When it comes to manufacturing processes, two of the most commonly used methods for creating parts are die casting and injection molding. Both are high-precision techniques that serve specific industries, but they differ significantly in their approach, materials, and suitability for various applications.
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a metal casting process in which molten metal is injected into a mold under high pressure. The mold, typically made of steel or another strong metal, is carefully crafted to create the desired shape. This method is particularly well-suited for producing complex metal parts with high precision. It is commonly used for applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where durability and strength are paramount.
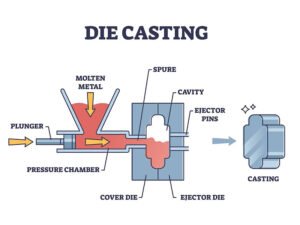
The Steps in Die Casting
- Mold Preparation and Clamping: The die, made from high-strength steel, is cleaned and lubricated to prevent sticking. The two halves of the die are then clamped together using a machine that applies significant force to keep them secure during injection.
- Injection of Molten Metal: Once the mold is ready, molten metal is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure. The pressure ensures that the molten metal fills every corner of the mold, even in complex geometries.
- Cooling and Solidification: After injection, the metal begins to cool and solidify. Cooling time can vary depending on the material used, but it typically takes a few seconds to a few minutes for the metal to harden completely.
- Ejection: After the metal has solidified, the mold opens, and the part is ejected. This is typically done using a hydraulic or mechanical system designed to safely remove the part from the mold.
- Finishing: Once the part is ejected, it may undergo various finishing processes such as trimming, polishing, or coating to improve its appearance or functionality.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding, on the other hand, is primarily used for plastic parts. In this
plastic injection molding service, plastic pellets are heated until they melt and then injected into a mold under high pressure. The process is very similar to die casting but involves plastics rather than metals. Injection molding is incredibly versatile and can be used to produce a wide range of products, from automotive components to medical devices.

The Steps in Injection Molding
- Mold Preparation and Heating: The mold, often made from aluminum or steel, is prepared by applying a release agent. It is then heated to a specific temperature to ensure proper material flow.
- Plastic Melting and Injection: Plastic pellets are fed into a heated barrel where a screw melts and mixes them. The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under pressure.
- Packing and Cooling: Additional pressure is applied to pack the material and prevent voids. Cooling lines circulate water or oil to solidify the plastic. The cooling time depends on the material and the thickness of the part.
- Mold Opening and Ejection: Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and ejector pins or mechanisms remove the part. Automation can handle this step for efficiency.
- Trimming and Secondary Operations: Gates and runners are removed. The part may undergo painting, assembly, or other finishes.

ZHongde Injection Molding Service
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting vs Injection Molding
When evaluating die casting vs injection molding, a comparison of advantages and disadvantages will help to make right decision. The table below summarizes key points based on industry standards.
Advantages
- Flexible design: Compared to die casting, injection molding is better suited for thin-walled, complex, and detailed plastic parts, without the draft angle limitations of metal die casting.
- Shorter production cycle and lower cost: Injection molding cycles are usually shorter than die casting, and mold costs are lower, making it suitable for small to medium batch production.
- Variety in surface finish and color: Plastic parts can achieve different colors, textures, and complex surface effects directly in the mold, while die-cast parts usually require additional painting or plating.
- Lightweight and corrosion-resistant: Plastic parts are lighter than metal and resistant to water, acids, and chemicals, suitable for applications that do not bear heavy mechanical loads.
Disadvantages
- Lower strength and heat resistance: Plastic parts cannot match die-cast metal parts in load-bearing capacity, wear resistance, or high-temperature performance.
- Dimensional stability affected by material: Plastic may expand or contract with temperature changes, making its precision and dimensional stability less reliable than metal die-cast parts.
- Limited for high-load or structural functional parts: Injection molding cannot fully replace die casting for components requiring high strength, wear resistance, or thermal conductivity.
Key Differences Between Die Casting and Injection Molding
While both die casting and injection molding are molding processes, they differ in several significant ways:
Materials Used
Die casting is primarily used for metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. These metals provide strength and durability, making die casting suitable for applications where high mechanical properties are required. Injection molding, on the other hand, is used for a variety of thermoplastic materials such as ABS, polystyrene, and polypropylene. These plastics are more suitable for applications that require lightweight, non-corrosive, and cost-effective materials.
Production Speed
Injection molding generally has faster cycle times, especially for smaller parts. This is due to the lower melting point of plastics and the shorter cooling times involved. Die casting, while also capable of high-volume production, tends to have longer cycle times due to the cooling and solidification process of metals.
Part Complexity
Injection molding can accommodate more intricate designs, particularly when dealing with smaller parts. The versatility of plastics allows for the creation of highly detailed shapes, while die casting is typically better suited for parts that need to be strong and resistant to high stress.
Tooling and Setup Costs
Die casting typically involves higher initial tooling costs because the molds need to be made from high-strength metals capable of withstanding the pressure of molten metal. Injection molding, while still requiring durable molds, tends to have lower initial tooling costs than die casting tools due to the ability to use less expensive materials for mold construction.
Process Pressure and Temperature
Die casting requires higher pressures (up to 100 MPa) and temperatures (around 700°F for aluminum). Injection molding operates at lower pressures and barrel temperatures (300–800°F).
Similarities Between Die Casting and Injection Molding
Despite the differences in material use and production processes, both die casting and injection molding share certain similarities. Both techniques rely on high-pressure injection of a material into a mold to create the desired part. Both processes are ideal for high-volume production, ensuring consistent quality and precision across large runs.
Injection Molding Expert Zhongde
Both die casting and injection molding offer advantages for different applications, and the right choice depends on factors such as material requirements, production speed, cost, and part complexity. At Zhongde, we specialize in plastic and rubber injection molding, providing high-quality, customized plastic components for a wide range of industries. The team can provide guidance on material selection and cost-effective solutions




